VMware NSX 4.X Professional V2 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년06월22일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 VMware 2V0-41.24 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 2V0-41.24 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 107개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
BGP will be configured on the T0 SR. Connect to the VRF for the T0 SR and run get bgp neighbor once connected to it. https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-Validated-Design/5.1/sddc-deployment-of-vmware-nsx-t-workload-domains-with-multiple-availability-zones/GUID-8BD4228A-75C6-4C60-80B4-538D4297E11A.html
For the BGP configuration on NSX-T, the Tier-0 Service Router (SR) is typically where BGP is configured.
To check the BGP neighbor status:
Connect to the VRF for the T0 SR, which is VRF 3 based on the provided output.
Run the command to get BGP neighbor status once connected to it.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the web search results, network segmentation is a feature of NSX that improves the security of today’s modern workloads by preventing lateral movement. Lateral movement is a technique used by attackers to move from one compromised system to another within a network, exploiting vulnerabilities or credentials. Network segmentation prevents lateral movement by dividing a network into smaller segments or zones, each with its own security policies and controls. This way, if one segment is compromised, the attacker cannot access other segments or resources.
NSX enables network segmentation by using micro-segmentation, which applies granular firewall rules at the virtual machine level, regardless of the physical network topology.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the web search results, error code 1001 is related to a time synchronization issue between the ESXi host and the NSX Manager. This can cause problems when configuring a time-based firewall rule, which requires the ESXi host and the NSX Manager to have the same time zone and NTP server settings. To resolve this error, you need to restart the NTP service on the ESXi host to synchronize the time with the NSX Manager. You can use the following command to restart the NTP service on the ESXi host:
/etc/init.d/ntpd restart
The other options are not valid solutions for this error. Reinstalling the NSX VIBs on the ESXi host will not fix the time synchronization issue. Changing the time zone on the ESXi host may cause more discrepancies with the NSX Manager. Reconfiguring the ESXi host with a local NTP server may not be compatible with the NSX Manager’s NTP server.
정답:
Explanation:
The service interface is a special-purpose port to enable services for mainly VLAN-based networks. North-south service insertion is another use case that requires a service interface to connect a partner appliance and redirect north-south traffic for partner services. Service interfaces are supported on both active-standby Tier-0 logical routers and Tier-1 routers. Firewall, NAT, and VPNs are supported on this interface. The service interface is also a downlink
정답:
Explanation:
The NSX Application Platform Deployment features are divided into three form factors: Evaluation, Standard, and Advanced. Each form factor determines which NSX features can be activated or installed on the platform1. The Evaluation form factor supports only NSX Intelligence, which provides network visibility and analytics for NSX-T environments2. The Standard form factor supports both NSX Intelligence and NSX Network Detection and Response, which provides network threat detection and response capabilities for NSX-T environments3. The Advanced form factor supports all four features: NSX Intelligence, NSX Network Detection and Response, NSX Malware Prevention, and NSX Metrics1.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/nsx-application-platform/GUID-85CD2728-8081-45CE-9A4A-D72F49779D6A.html
정답:
Explanation:
according to the VMware NSX Documentation, these are the three parameters that must match in order to establish an OSPF neighbor relationship with an upstream router on a tier-0 gateway:
MTU of the Uplink: The maximum transmission unit (MTU) of the uplink interface must match the MTU of the upstream router interface. Otherwise, OSPF packets may be fragmented or dropped, causing neighbor adjacency issues.
Subnet mask: The subnet mask of the uplink interface must match the subnet mask of the upstream router interface. Otherwise, OSPF packets may not reach the correct destination or be rejected by the upstream router.
Area ID: The area ID of the uplink interface must match the area ID of the upstream router interface.
Otherwise, OSPF packets may be ignored or discarded by the upstream router.
https://www.computernetworkingnotes.com/ccna-study-guide/ospf-neighborship-condition-and-requirement.html
정답:
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, these are two of the use cases for Distributed Intrusion Detection, which is a feature of NSX Network Detection and Response:
Quarantine workloads based on vulnerabilities: You can use Distributed Intrusion Detection to detect
vulnerabilities in your workloads and apply quarantine actions to isolate them from the network until they are remediated.
Identify security vulnerabilities in the workloads: You can use Distributed Intrusion Detection to scan your workloads for known vulnerabilities and generate reports that show the severity, impact, and remediation steps for each vulnerability.
정답:
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation, these are the prerequisites for adding nodes to an NSX Management Cluster using the NSX UI:
All nodes must be in the same subnet and have IP connectivity with each other.
A compute manager must be configured and associated with the NSX Manager node.
The NSX Manager node must have a valid license.
The NSX Manager node must have a valid certificate.
정답: 
Explanation:
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-Intelligence/4.0/user-guide/GUID-DC78552B-2CC4-410D-A6C9-3FE0DCEE545B.html
정답:
Explanation:
According to the web search results, VMware Aria Operations Networks (formerly vRealize Network Insight) is a network monitoring tool that can help monitor, discover and analyze networks and applications across clouds1. It can also provide enhanced troubleshooting and visibility for physical and virtual networks2.
The other options are either incorrect or not relevant for identifying problems in a physical network. VMware Aria Automation is a cloud automation platform that can help automate the delivery of IT services. VMware Aria Orchestrator is a cloud orchestration tool that can help automate workflows and integrate with other systems. VMware Site Recovery Manager is a disaster recovery solution that can help protect and recover virtual machines from site failures.
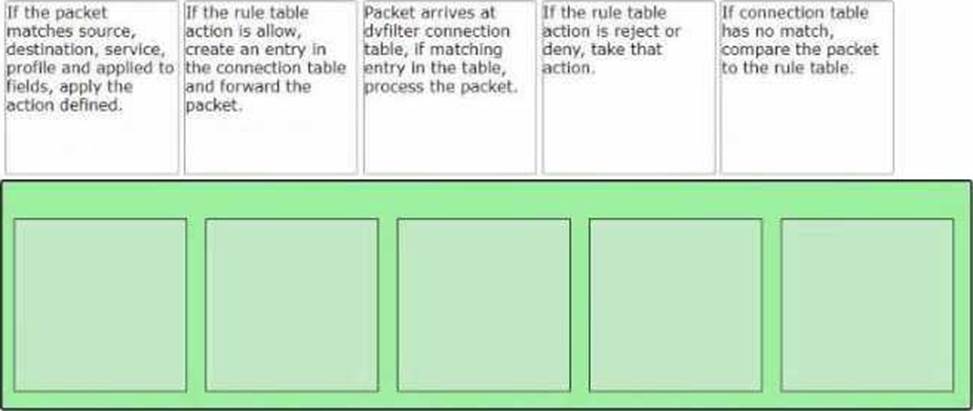
정답: 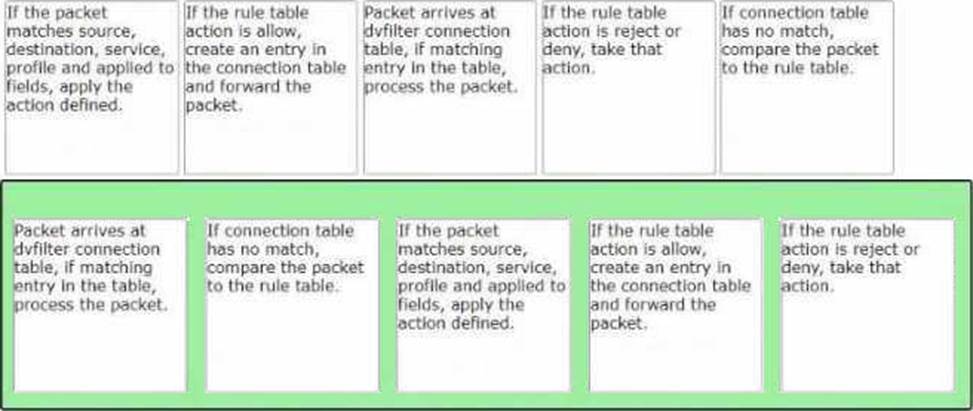
Explanation:
The correct order of the rule processing steps of the Distributed Firewall is as follows:
Packet arrives at vfilter connection table. If matching entry in the table, process the packet.
If connection table has no match, compare the packet to the rule table.
If the packet matches source, destination, service, profile and applied to fields, apply the action defined.
If the rule table action is allow, create an entry in the connection table and forward the packet.
If the rule table action is reject or deny, take that action.
This order is based on the description of how the Distributed Firewall works in the web search results1. The first step is to check if there is an existing connection entry for the packet in the vfilter connection table, which is a cache of flow entries for rules with an allow action. If there is a match, the packet is processed according to the connection entry. If there is no match, the packet is compared to the rule table, which contains all the security policy rules. The rules are evaluated from top to bottom until a match is found. The match criteria include source, destination, service, profile and applied to fields. The action defined by the matching rule is applied to the packet. The action can be allow, reject or deny. If the action is allow, a new connection entry is created for the packet and the packet is forwarded to its destination. If the action is reject or deny, the packet is dropped and an ICMP message or a TCP reset message is sent back to the source.
정답:
Explanation:
The correct answers are
A. Files and anti-malware (file) events from the NSX Edge nodes and the Security Analyzer,
D. IDS/IPS events from the ESXi hosts and NSX Edge nodes, and
E. Suspicious Traffic Detection events from NSX Intelligence. According to the VMware NSX Documentation3, these are the three data collection sources that are used by NSX Network Detection and Response to create correlations/intrusion campaigns.
The other options are incorrect or not supported by NSX Network Detection and Response. East-West anti-malware events from the ESXi hosts are not collected by NSX Network Detection and Response3. Distributed Firewall flow data from the ESXi hosts are not used for correlation/intrusion campaigns by NSX Network Detection and Response3.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX-T-Data-Center/3.2/administration/GUID-14BBE50D-9931-4719-8FA7-884539C0D277.html
정답:
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation2, the FABRIC message ID (msgld) captures messages related to NSX host preparation events, such as installation, upgrade, or uninstallation of NSX components on ESXi hosts. The syslog export configuration command for NSX host preparation events would look something like this:
set service syslog export FABRIC
The other options are either incorrect or not relevant for NSX host preparation events. MONITORING
captures messages related to NSX monitoring features, such as alarms and system events2. SYSTEM
captures messages related to NSX system events, such as login, logout, or configuration
changes2. GROUPING captures messages related to NSX grouping objects, such as security groups,
security tags, or IP sets2.
https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.1/administration/GUID-CC18C0E3-D076-41AA-8B8C-133650FDC2E7.html
정답:
Explanation:
Route Aggregation and and D) BGP neighbours are available when configuring BGP in a VRF. "Route
distribution" does not exist, what you can do is a "Route Re-Distribution" via BGP. https://docs.vmware.com/en/VMware-NSX/4.1/administration/GUID-4CB5796A-1CED-4F0E-ADE0-72BF7B3F762C.html
정답:
Explanation:
According to the VMware NSX Documentation1, a segment is mapped to a unique Geneve segment that is distributed across the ESXi hosts in a transport zone. The Geneve segment uses a virtual network identifier (VNI) as an overlay network identifier. The VNI ID can be used to identify overlay segments in an NSX environment if troubleshooting is required.