Certified Ethical Hacker Exam (CEHv12) 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년10월19일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 EC-Council 312-50v12 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 312-50v12 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 503개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
정답:
정답:
정답:
Explanation:
Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation can be defined as taking steps to reduce adverse effects. There are four types of risk mitigation strategies that hold unique to Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery. When mitigating risk, it’s important to develop a strategy that closely relates to and matches your company’s profile.
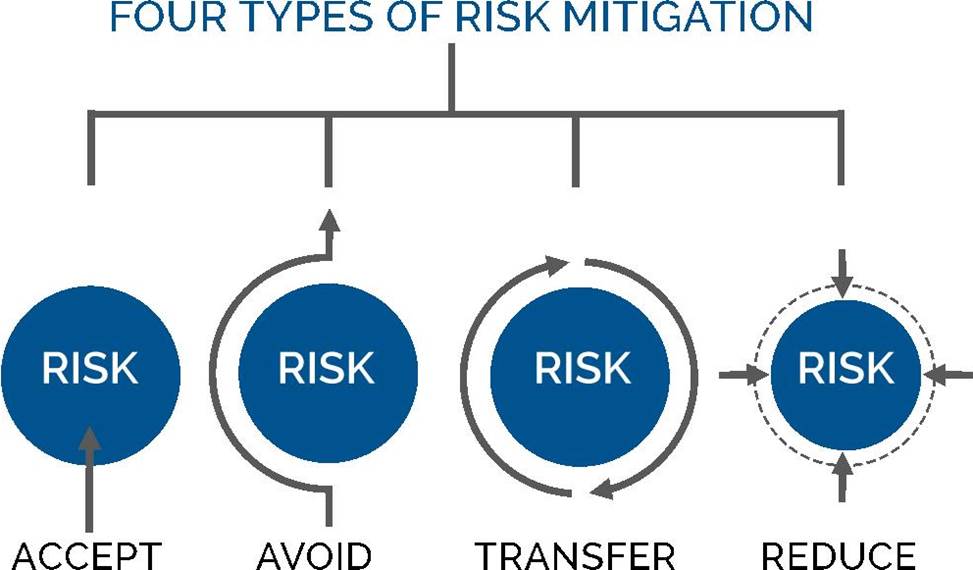
A picture containing diagram
Description automatically generated
Risk Acceptance
Risk acceptance does not reduce any effects; however, it is still considered a strategy. This strategy is a common option when the cost of other risk management options such as avoidance or limitation may outweigh the cost of the risk itself. A company that doesn’t want to spend a lot of money on avoiding risks that do not have a high possibility of occurring will use the risk acceptance strategy.
Risk Avoidance
Risk avoidance is the opposite of risk acceptance. It is the action that avoids any exposure
to the risk whatsoever. It’s important to note that risk avoidance is usually the most expensive of all risk mitigation options.
Risk Limitation
Risk limitation is the most common risk management strategy used by businesses. This strategy limits a company’s exposure by taking some action. It is a strategy employing a bit of risk acceptance and a bit of risk avoidance or an average of both. An example of risk limitation would be a company accepting that a disk drive may fail and avoiding a long period of failure by having backups.
Risk Transference
Risk transference is the involvement of handing risk off to a willing third party. For example, numerous companies outsource certain operations such as customer service, payroll services, etc. This can be beneficial for a company if a transferred risk is not a core competency of that company. It can also be used so a company can focus more on its core competencies.
정답:
정답:
Explanation:
Email spoofing is the fabrication of an email header in the hopes of duping the recipient into thinking the email originated from someone or somewhere other than the intended source. Because core email protocols do not have a built-in method of authentication, it is common for spam and phishing emails to use said spoofing to trick the recipient into trusting the origin of the message.
The ultimate goal of email spoofing is to get recipients to open, and possibly even respond to, a solicitation. Although the spoofed messages are usually just a nuisance requiring little action besides removal, the more malicious varieties can cause significant problems and sometimes pose a real security threat.
정답:
정답:
정답:
정답:
Explanation:
Social engineering is the term used for a broad range of malicious activities accomplished through human interactions. It uses psychological manipulation to trick users into making security mistakes or giving away sensitive information.
Social engineering attacks typically involve some form of psychological manipulation, fooling otherwise unsuspecting users or employees into handing over confidential or sensitive data. Commonly, social engineering involves email or other communication that invokes urgency, fear, or similar emotions in the victim, leading the victim to promptly reveal sensitive information, click a malicious link, or open a malicious file. Because social engineering involves a human element, preventing these attacks can be tricky for enterprises.
정답:
정답:
정답:
Explanation:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Residual_risk
The residual risk is the risk or danger of an action or an event, a method or a (technical) process that, although being abreast with science, still conceives these dangers, even if all theoretically possible safety measures would be applied (scientifically conceivable measures); in other words, the amount of risk left over after natural or inherent risks have been reduced by risk controls.
・ Residual risk = (Inherent risk) C (impact of risk controls)
정답:
정답: