Administering a SQL Database Infrastructure 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년10월08일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 Microsoft 70-764 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 70-764 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 451개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
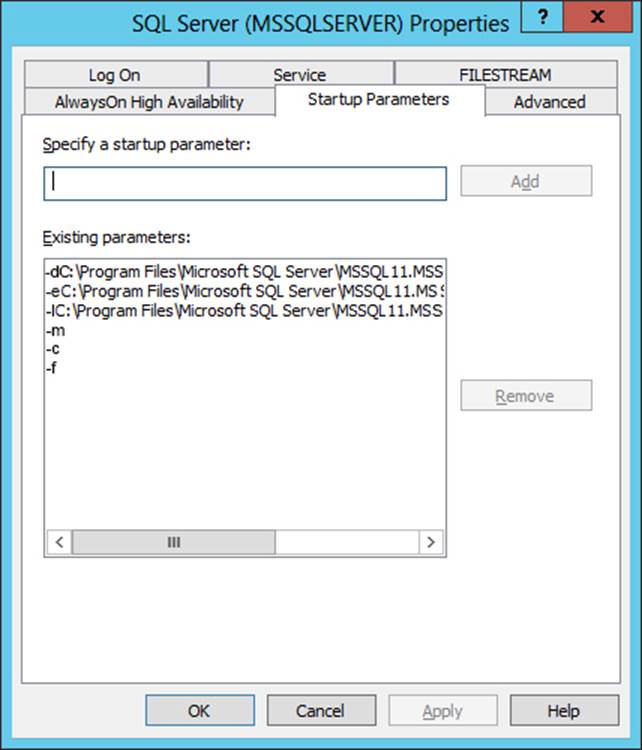
정답: 
Explanation:
Box 1: single-user
The startup option -m starts an instance of SQL Server in single-user mode.
Box 2: sysadmin
Starting SQL Server in single-user mode enables anymember of the computer's local Administrators group to connect to the instance of SQL Server as a member of the sysadmin fixed server role.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/configure-windows/database-engine-service-startup-options
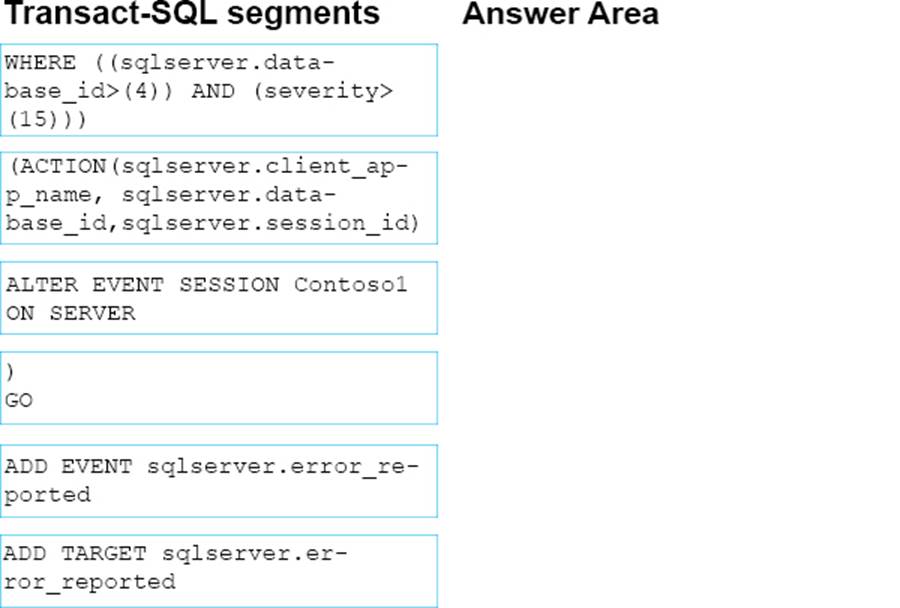
정답: 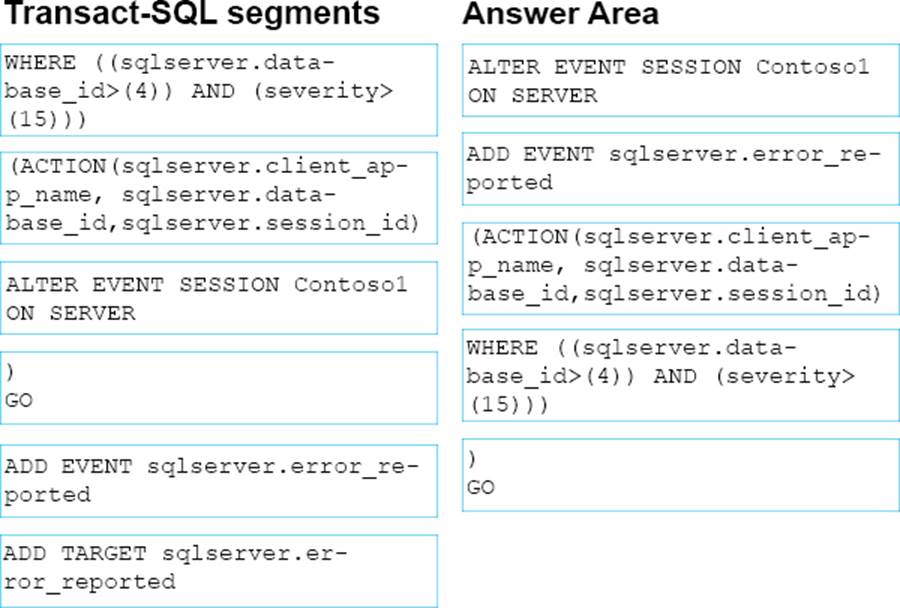
Explanation:
Step 1: ALTER EVENT SESSION Contoso1 ON SERVER
Step 2: ADD EVENT …
Step 3: (ACTION ...
Step 4: WHERE...
Step 5: ) GO
Example: To start an Extended Events sessions in order to trap SQL Server errors with severity greater than 10,just run the following script:
CREATE EVENT SESSION [error_trap] ON SERVER
ADD EVENT sqlserver.error_reported
(
ACTION (package0.collect_system_time,package0.last_error,sqlserver.client_app_name,sqlserver.client_hostname,sqlserver.database_id,sqlserver.database_name,sqlserver.nt_username, sqlserver.plan_handle,sqlserver.query_hash,sqlserver.session_id,sqlserver.sql_text,sqlserver.tsql_frame,sqlserver.tsql_stack,sqlserver.username)
WHERE ([severity]>10)
)
ADD TARGET package0.event_file
(
SET filename=N'D:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL11.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\XEvents\error_trap.xel'
)
WITH
(
STARTUP_STATE=OFF
)
GO
References: http://sqlblog.com/blogs/davide_mauri/archive/2013/03/17/trapping-sql-server-errors-with-extended-events.aspx
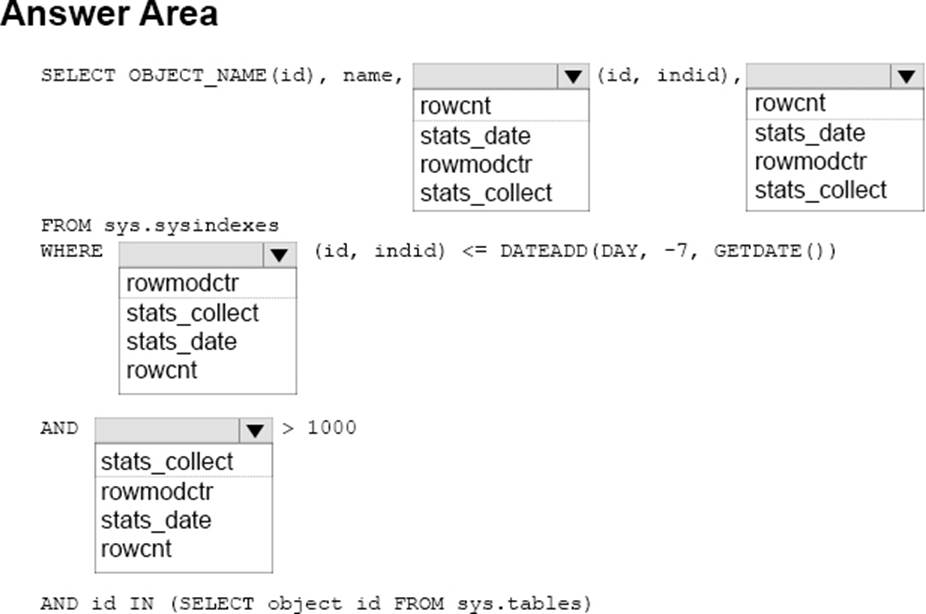
정답: 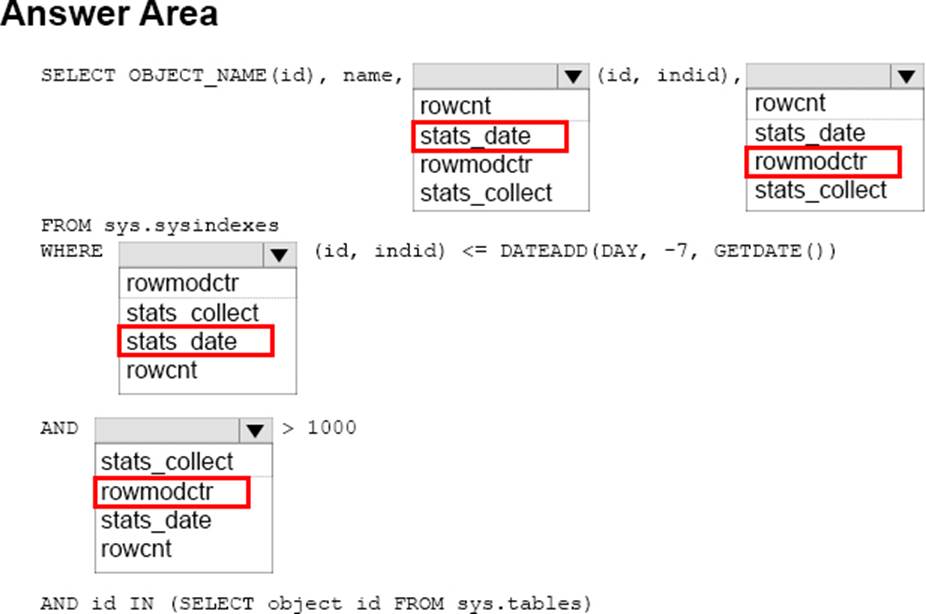
Explanation:
Box 1: stats_date
See example below.
Box 2: rowmodctr
See examplebelow.
Box 3: stats_date
You need to identify statistics that have not been updated for a week.
Box 4: rowmodctr
You need to identify that more than 1,000 rows changed.
Rowmodctr counts the total number of inserted, deleted, or updated rows since the last time statistics were updated for the table.
Example: We will query every statistics object which was not updated in the last day and has rows modified since the last update. We will use the rowmodctr field of sys.sysindexes because it shows how many rows were inserted, updated or deleted since the last update occurred. Please note that it is not always 100% accurate in SQL Server 2005 and later, but it can be used to check if any rows were modified.
--Get the list of outdated statistics
SELECTOBJECT_NAME(id),name,STATS_DATE(id, indid),rowmodctr
FROM sys.sysindexes
WHERE STATS_DATE (id, indid)<=DATEADD(DAY,-1,GETDATE())
AND rowmodctr>0
AND id IN (SELECT object_id FROM sys.tables)
GO
After collecting this information, we can decide which statistics require an update.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/system-compatibility-views/sys-sysindexes-transact-sql
https://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertip/2628/how-to-find-outdated-statistics-in-sql-server-2008/
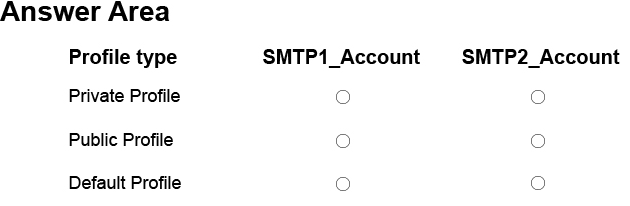
정답: 
Explanation:
SMTP1_Account1: Private Profile
When no profile_name is specified, sp_send_dbmail uses the default private profile for the current user. If the user does not have a default private profile, sp_send_dbmail uses the default public profile for the msdb database.
SMTP1_Account2: Default Profile
Execute permissions forsp_send_dbmail default to all members of the DatabaseMailUser database role in the msdb database.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/system-stored-procedures/sp-send-dbmail-transact-sql
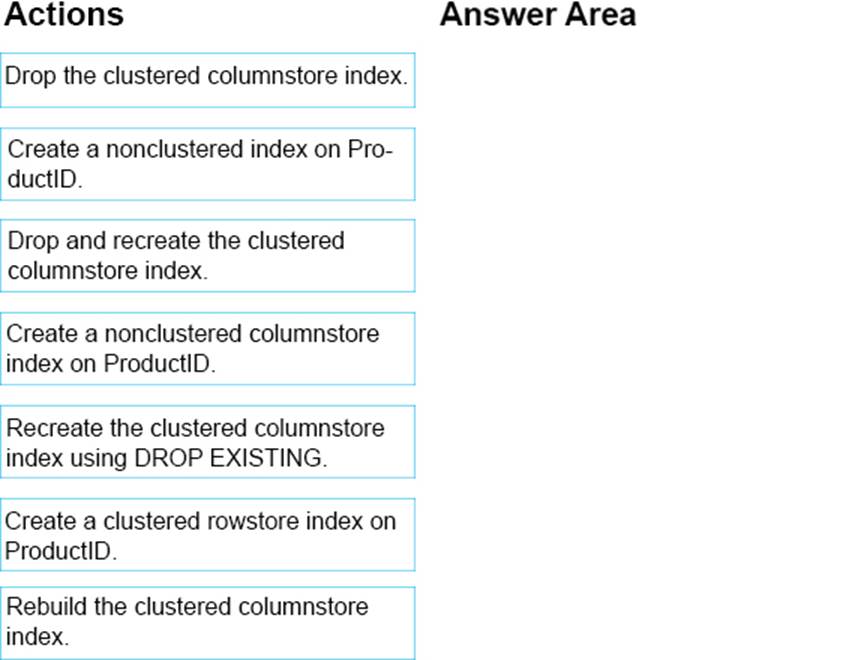
정답: 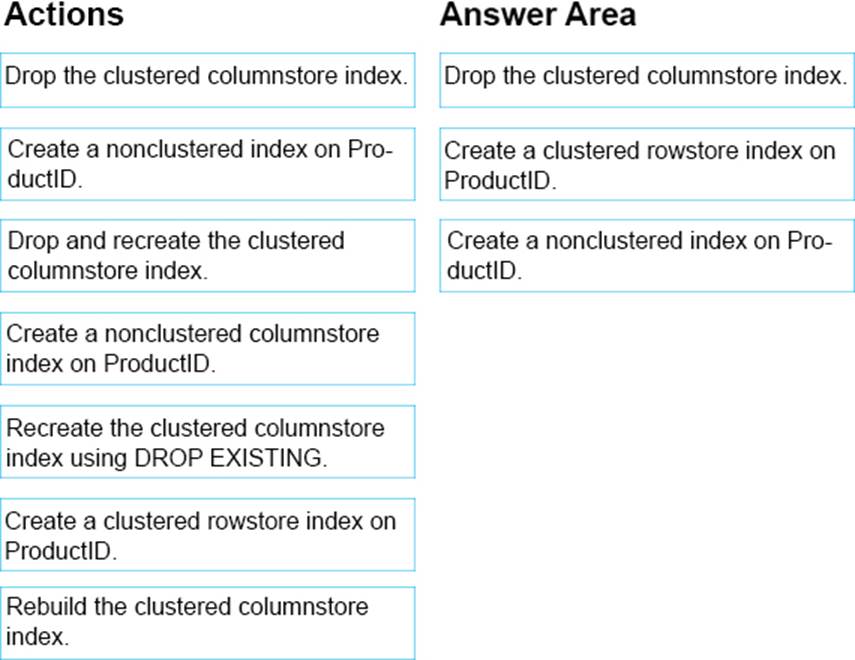
Explanation:
Step 1: Drop the clustered columnstore index
Step 2: Create a clustered rowstore index on ProductID.
Rowstore indexes perform best on queries that seek into the data, searching for a particular value, or for queries on a small range of values. Use rowstore indexes with transactional workloads since they tend to require mostly table seeks instead of table scans.
Step 3: Create a nonclustered index on ProductID

정답: 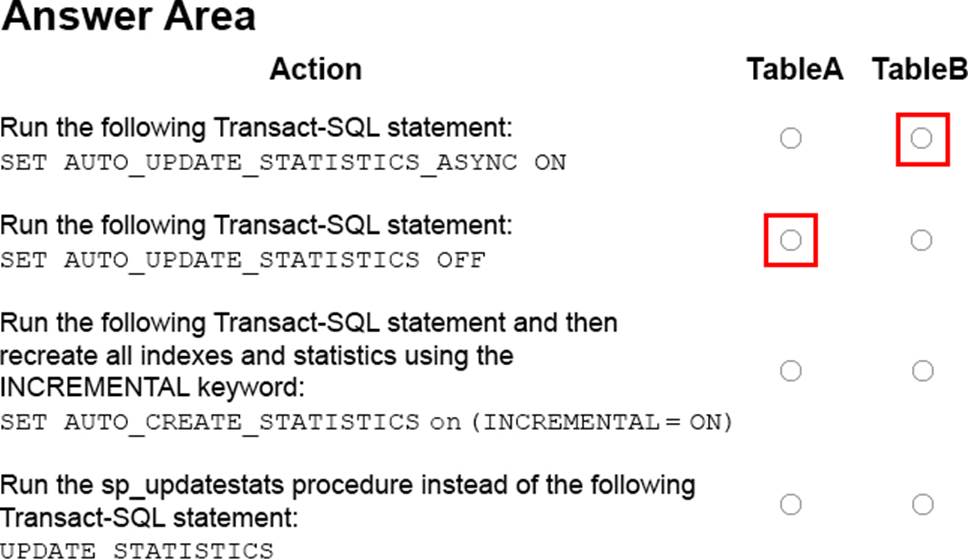
Explanation:
Table A: Auto_update statistics off
Table A does not change much. There is no need to update the statistics on this table.
Table B: SET AUTO_UPDATE_STATISTICS_ASYNC ON
You can set the database to update statistics asynchronously:
ALTER DATABASE YourDBName
SET AUTO_UPDATE_STATISTICS_ASYNC ON
If you enable this option then the Query Optimizer will run the query first and update the outdated statistics afterwards. When you set this option to OFF, the Query Optimizer will update the outdated statistics before compiling the query. This option can be useful in OLTP environments
References: https://www.mssqltips.com/sqlservertip/2766/sql-server-auto-update-and-auto-create-statistics-options/
정답:
Explanation:
Stale Query Threshold (Days): Time-based cleanup policy that controls the retention period of persisted runtime statistics and inactive queries. By default, Query Store is configured to keep the data for 30 days which may be unnecessarily long for your scenario. Avoid keeping historical data that you do not plan to use. This will reduce changes to read-only status. The size of Query Store data as well as the time to detect and mitigate the issue will be more predictable. Use Management Studio or the following script to configure time-based cleanup policy:
ALTER DATABASE [QueryStoreDB] SET QUERY_STORE (CLEANUP_POLICY = (STALE_QUERY_THRESHOLD_DAYS = 14));
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/performance/best-practicewith-the-query-store
정답:
Explanation:
To encrypt during backup, you must specify an encryption algorithm, and an encryptor to secure the encryption key. The following are the supported encryption options: Encryption Algorithm: The supported encryption algorithms are: AES 128, AES 192, AES 256, and Triple DES Encryptor: A certificate or asymmetric Key
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/backup-restore/backupencryption

정답:
Explanation:
The return value can either be a scalar (single) value or a table. SELECT 1 just selects a 1 for every row, of course.
What it's used for in this case is testing whether any rows exist that match the criteria: if a row exists that matches the WHERE clause, then it returns 1, otherwise it returns nothing. Specify the WITH SCHEMABINDING clause when you are creating the function. This ensures that the objects referenced in the function definition cannot be modified unless the function is also modified.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/statements/create-function-transact-sql
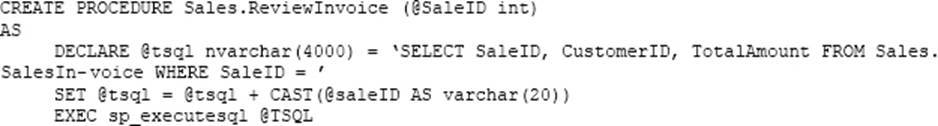
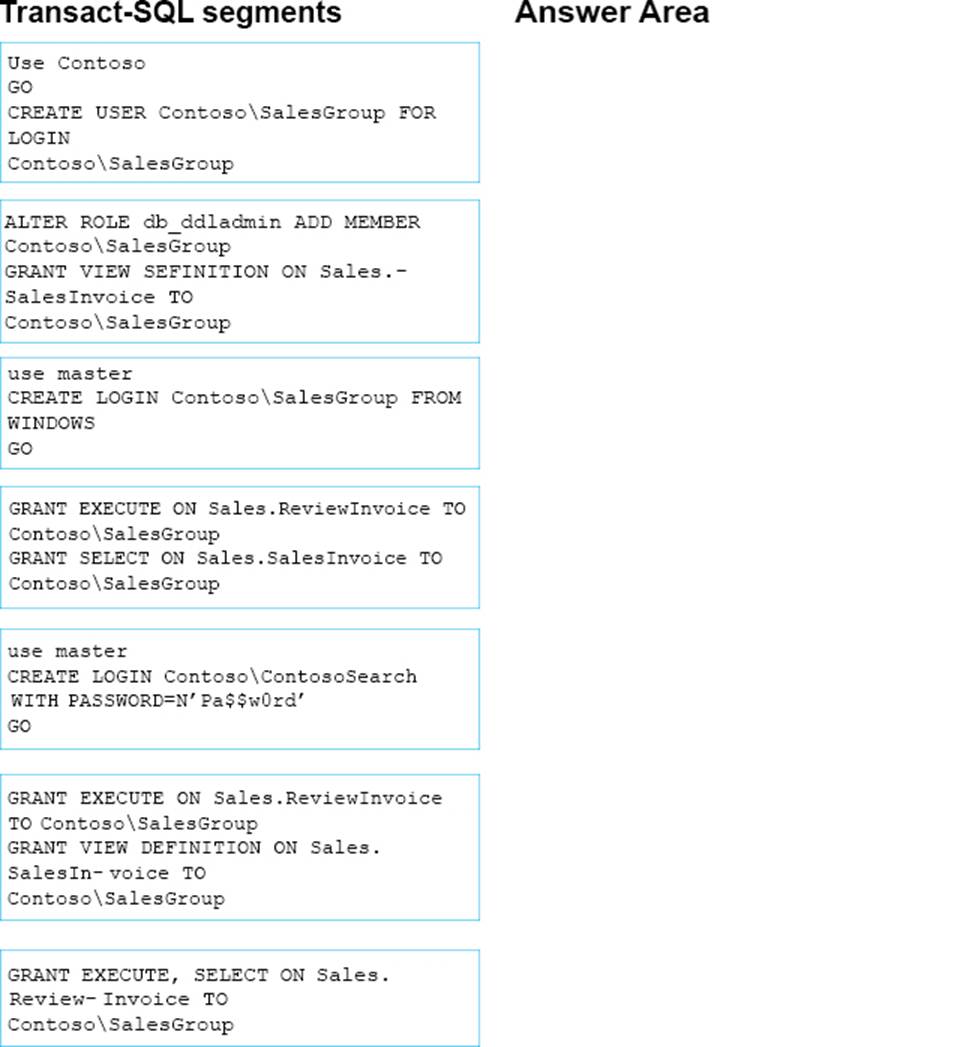
정답: 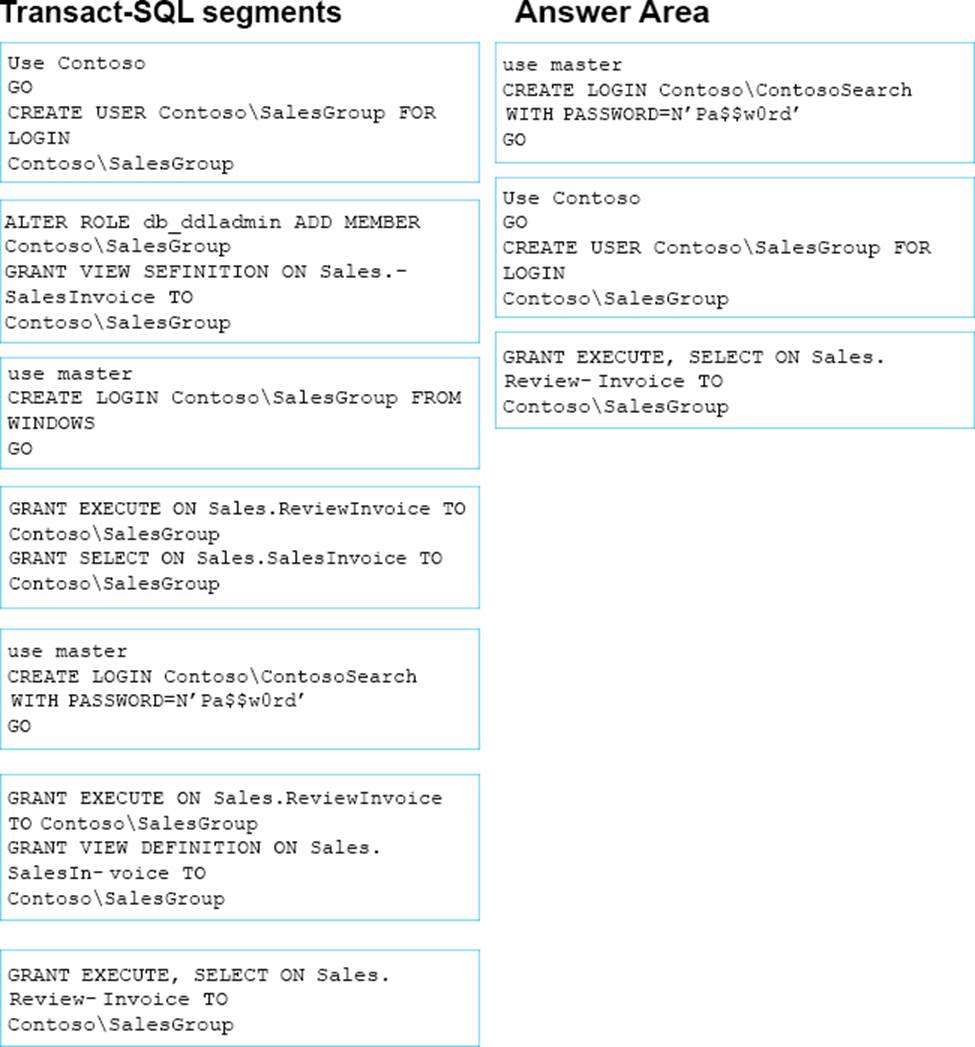
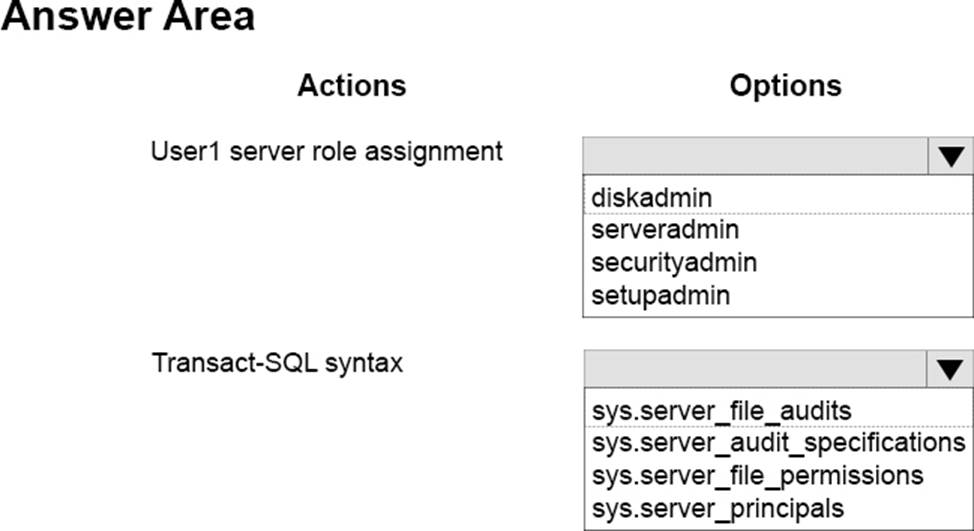
정답: 
Explanation:
Box 1: securityadmin
To access log files for instances of SQL Server that are online, this requires membership in the securityadmin fixed server role.
Box 2: sys.server_audit_specifications
sys.server_audit_specifications contains information about the server audit specifications in a SQL Server audit on a server instance.
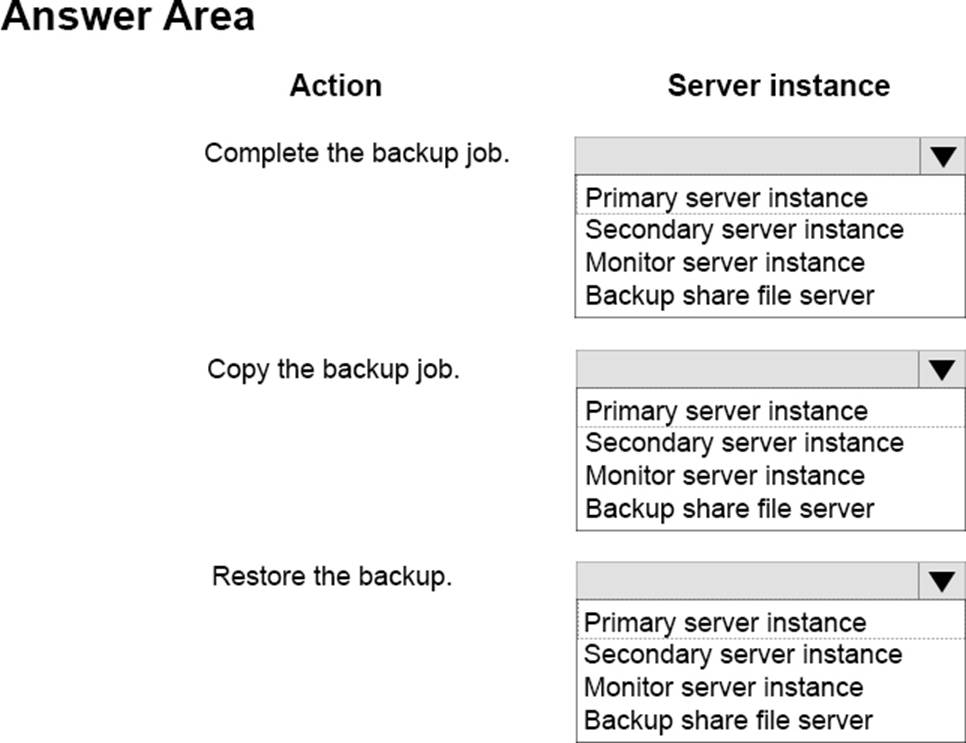
정답: 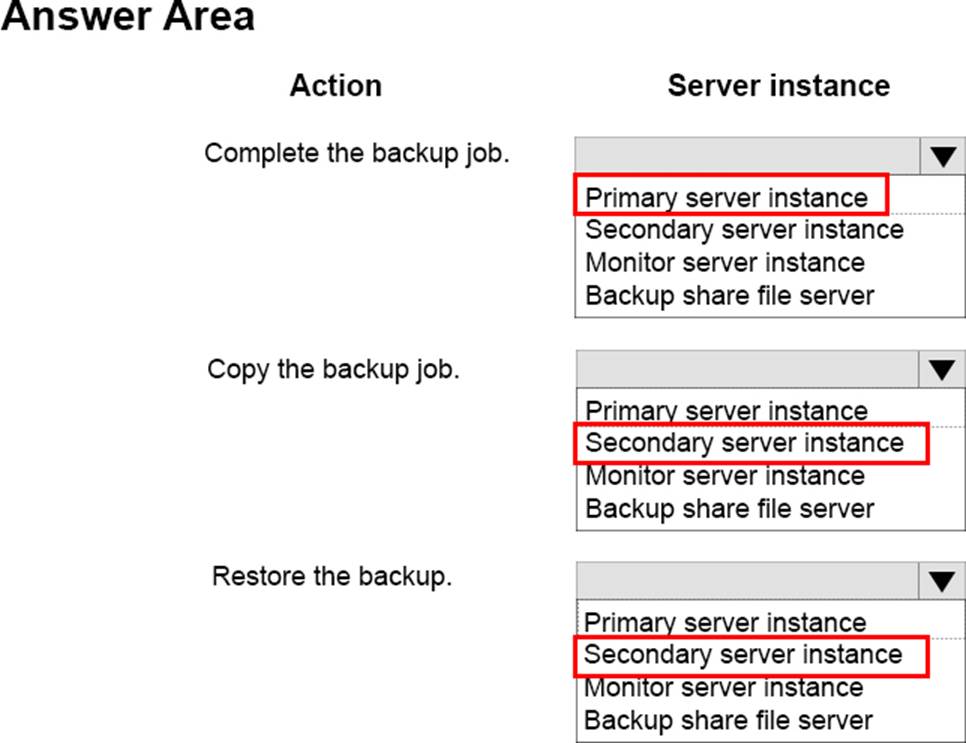
Explanation:
Note: Before you configure log shipping, you must create a share to make the transaction log backups available to the secondary server.
SQL Server Log shipping allows you to automatically send transaction log backups from a primary database on a primary server instance to one or more secondary databases on separate secondary server instances. The transaction log backups are applied to each of the secondary databases individually. An optional third server instance, known as the monitor server, records the history and status of backup and restore operations and, optionally, raises alerts if these operations fail to occur as scheduled.
Box 1: Primary server instance.
The primary server instance runs the backup job to back up the transaction log on the primary database.
backup job: A SQL Server Agent job that performs the backup operation, logs history to the local server and the monitor server, and deletes old backup files and history information. When log shipping is enabled, the job category "Log Shipping Backup" is created on the primary server instance.
Box 2: Secondary server instance
Each of the three secondary server instances runs its own copy job to copy the primary log-backup file to its own local destination folder.
copy job: A SQL Server Agent job that copies the backup files from the primary server to a configurable destination on the secondary server and logs history on the secondary server and the monitor server. When log shipping is enabled on a database, the job category "Log Shipping Copy" is created on each secondary server in a log shipping configuration.
Box 3: Secondary server instance.
Each secondary server instance runs its own restore job to restore the log backup from the local destination folder onto the local secondary database.
restore job: A SQL Server Agent job that restores the copied backup files to the secondary databases. It logs history on the local server and the monitor server, and deletes old files and old history information. When log shipping is enabled on a database, the job category "Log Shipping Restore" is created on the secondary server instance.
References: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/log-shipping/about-log-shipping-sql-server
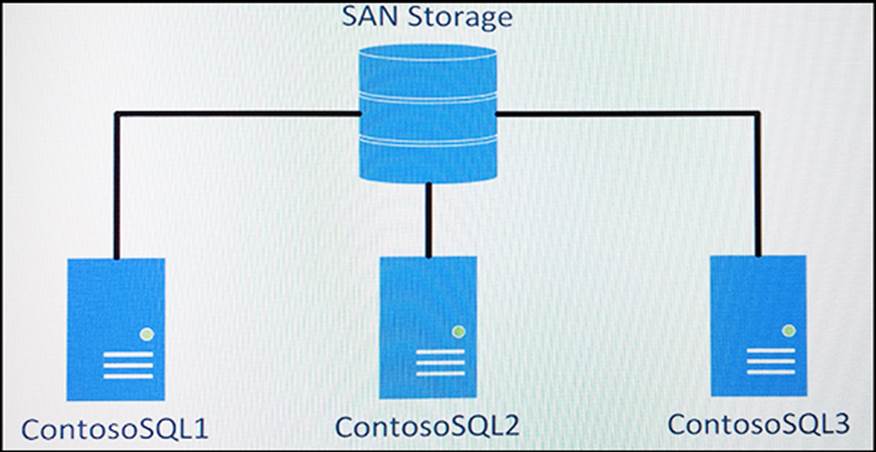


정답: 
Explanation:
Box 1: Yes
tempdb on local storage. FCIs now support placement of tempdb on local non-shared storage, such as a local solid-state-drive, potentially offloading a significant amount of I/O from a shared SAN.
Prior to SQL Server 2012, FCIs required tempdb to be located on a symmetrical shared storage volume that failed over with other system databases.
Box 2: No
The VNN is set on the group level, not on the instance level.
Database client applications can connect directly to a SQL Server instance network name, or they may connect to a virtual network name (VNN) that is bound to an availability group listener. The VNN abstracts the WSFC cluster and availability group topology, logically redirecting connection requests to the appropriate SQL Server instance and database replica.
The logical topology of a representative AlwaysOn solution is illustrated in this diagram:
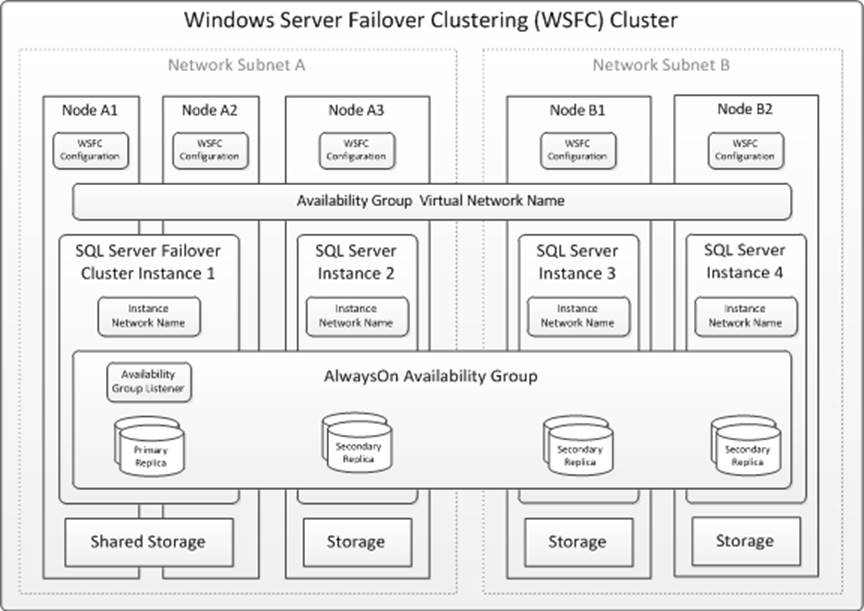
Box 3: No
You don't configure the SAN from a SQL Server, instead you can use a Microsoft Server server.
References: http://download.microsoft.com/download/d/2/0/d20e1c5f-72ea-4505-9f26-fef9550efd44/microsoft%20sql%20server%20alwayson%20solutions%20guide%20for%20high%20availability%20and%20disaster%20recovery.docx


정답: 
Explanation:
Box 1: is
The dedicated backup file share is \\localhost\Backup
Box 2: does not run
The only thing with a name related to ADATM-SQL11 is the schedule name.
Box 3: 72 hours
4320 minutes equals 72 hours.
Note: @backup_retention_period= ] backup_retention_period
Isthe length of time, in minutes, to retain the log backup file in the backup directory on the primary server. backup_retention_period is int, with no default, and cannot be NULL.
Box 4: 15 minutes.
[ @freq_subday_type = ] freq_subday_type
Specifies the units for freq_subday_interval. freq_subday_typeis int, with a default of 0, and can be one of these values.
Here it is 4, which means minutes.
[ @freq_subday_interval = ] freq_subday_interval
The number of freq_subday_type periods to occur between eachexecution of a job. freq_subday_intervalis int, with a default of 0.
Note: Interval should be longer than 10 seconds. freq_subday_interval is ignored in those cases where freq_subday_type is equal to 1.
Here it is 15.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/system-stored-procedures/sp-add-schedule-transact-sql
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/system-stored-procedures/sp-add-log-shipping-primary-database-transact-sql

정답: 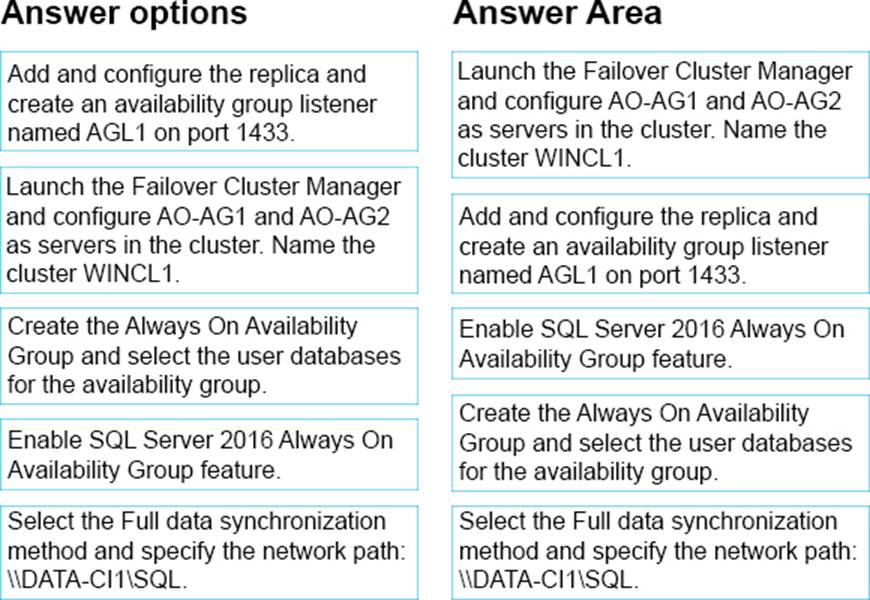
Explanation:
Step 1: Launch the Failover Cluster Manager and..
To support theAlways On availability groups feature, ensure that every computer that is to participate in one or more availability groups meets requirements including:
* Ensure that each computer is a node in a WSFC (Windows Server Failover Clustering).
Step 2: Add andconfigure the replica and…
All the server instances that host availability replicas for an availability group must use the same SQL Server collation.
Step 3: Enable the SQL Server 2016 Always On Availability Group feature.
Enable the Always On availability groups feature on each server instance that will host an availability replica for any availability group. On a given computer, you can enable as many server instances for Always On availability groups as your SQL Server installation supports.
Step 4: Create the Always On Availability Group and..
Using Transact-SQL to create or configure an availability group listener
Step 5: Select the Full data synchronization method and…
References: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj899851(v=sc.12).aspx https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/database-engine/availability-groups/windows/create-orconfigure-an-availability-group-listener-sql-server