Expert - PowerMax and VMAX All Flash Solutions 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년04월16일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 DELL EMC DEE-1111 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 DEE-1111 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 54개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
The most likely cause of this behavior is QFULL responses of the FA ports. When additional hosts are zoned to certain front-end adapters, the FA ports may not be able to handle the increased I/O requests, resulting in QFULL responses. This can cause non-linear variations in throughput and sometimes a drop in throughput of more than 20%.
Reference: Dell EMC PowerMax: Service Levels for PowerMaxOS
정답:
Explanation:
When maintenance tasks at the R1 data center require the array to be offline, a Swap operation should be executed on the Metro RDF pairs. This operation allows for a planned outage without affecting application I/O by swapping the roles of R1 and R2 devices.
정답:
Explanation:
The maximum retention period for the SLO Compliance Report is 6 months. This means that data older than 6 months will not be available in the report
정답:
Explanation:
For an SRDF/Metro personality swap, the SRDF/Metro devices must be Read/Write (RW) on the link.
This ensures that data can be read from and written to the devices during the swap operation.
Reference: SRDF/Metro overview | Dell EMC PowerMax and VMAX All Flash: SRDF/Metro Overview and Best Practices, Understanding bias | Dell EMC PowerMax and VMAX All Flash: SRDF/Metro Overview and Best Practices
정답:
Explanation:
Before configuring Access Control, the security administrator must define the User Access ID for the Admin User. This is a necessary step to ensure that the administrator has the necessary permissions to perform this operation.
PowerMax & VMAX All-Flash Storage Technical Documentation, Dell EMC PowerMax and VMAX All Flash: Embedded Management
정답:
Explanation:
In an SRDF/Metro configuration with bias setting, if there is a failure at the R1 array (which is configured as the bias side), the R2 device automatically becomes the active device. This means that even if there’s a failure on the R1 side, operations can continue on the R2 side without interruption, ensuring high availability.
https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/l/dell-emc-powermax-and-vmax-all-flash-srdf-metro-overview-and-best-practices-1/understanding-bias
정답:
Explanation:
Fast Write is a Dell EMC technology that improves Fibre Channel (FC) replication between sites in a
SRDF/S configuration. When a write I/O is issued by the host to the R1 device, SRDF with Fast Write
acknowledges the write to the host as soon as the data is stored in the R1’s cache and transmitted to
the R2’s cache. This results in reduced latency and improved performance for FC replication between
sites.
https://www.delltechnologies.com/asset/en-us/products/storage/industry-market/h17118_dell_emc_powermax_family_overview.pdf
https://infohub.delltechnologies.com/l/dell-emc-powermax-and-vmax-all-flash-srdf-metro-overview-and-best-practices-1/srdf-metro-overview/
정답:
Explanation:
The -precopy option in the relink command can be used when you want to start copying data to the target devices immediately after the link operation. This can be useful in situations where additional volumes have been added, increasing the link to full copy time. By using -precopy, you ensure that the data starts copying immediately, preventing potential issues.
정답: 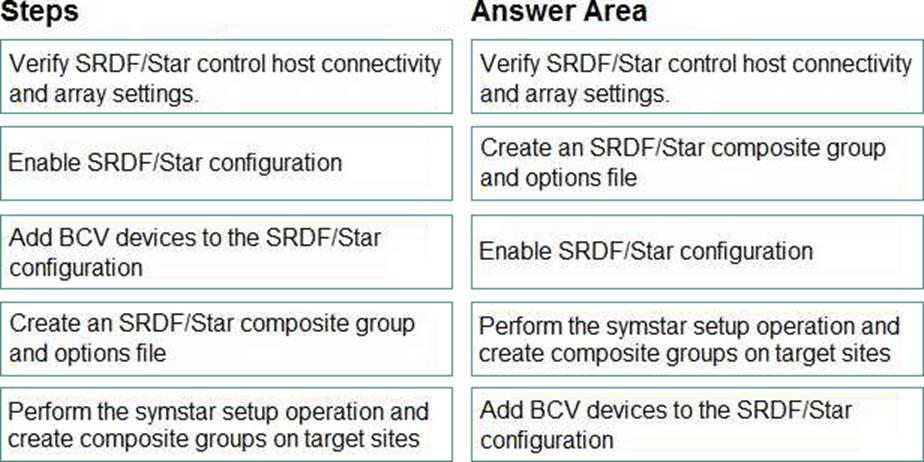
Explanation:
The correct sequence of steps to configure and bring up an SRDF/Star environment is as follows: Verify SRDF/Star control host connectivity and array settings. This step involves checking the network connectivity between the control host and the three arrays involved in the SRDF/Star configuration, as well as verifying the array settings such as RDF mode, RDF consistency, and RDF emulation. The control host is the host that runs the Solutions Enabler SYMCLI commands to manage the SRDF/Star configuration. The three arrays are the primary array, the secondary array, and the tertiary array.1 Enable SRDF/Star configuration. This step involves enabling the SRDF/Star feature on the primary array using the symstar enable command. This command also creates a STAR control device group on the primary array, which contains a single device that acts as a control point for the SRDF/Star configuration. The STAR control device group must have a unique name and number across all arrays.1
Add BCV devices to the SRDF/Star configuration. This step involves adding Business Continuance Volume (BCV) devices to the STAR control device group on the primary array using the symstar add bcv command. BCV devices are local copies of data that can be used for backup, restore, or testing purposes. BCV devices are required for SRDF/Star configurations to enable fast recovery in case of a disaster. The number of BCV devices must match the number of R1 devices in the SRDF/Star configuration.1
Create an SRDF/Star composite group and options file. This step involves creating an SRDF/Star composite group on the control host using the symstar create command. An SRDF/Star composite group is a logical grouping of devices that span across three arrays and have different SRDF roles: R11, R21, and R22. An R11 device is an R1 device that is paired with another R1 device in a different SRDF group. An R21 device is an R2 device that is paired with another R1 device in a different SRDF group. An R22 device is an R2 device that is paired with another R2 device in a different SRDF group. The symstar create command also creates an options file that contains various parameters for the SRDF/Star configuration, such as RDF mode, RDF consistency, RDF emulation, and bias setting.1 Perform the symstar setup operation and create composite groups on target sites. This step involves performing the symstar setup operation on the control host using the symstar setup command. This command establishes the SRDF/Star configuration by creating RDF pairs between devices in different arrays, creating RDF groups on each array, creating composite groups on each array, and synchronizing data across all devices. The symstar setup command also creates composite groups on the secondary and tertiary arrays using the same name and number as the composite group on the primary array.1
Reference: Dell EMC Solutions Enabler 9.2 SRDF Family CLI User Guide
정답:
Explanation:
When vWitness and Array Witness options are deployed in the same operating environment simultaneously, SRDF/Metro favors the Witness option over the Array Witness option. This is because the Witness option provides a higher level of protection against split-brain scenarios and data loss than the Array Witness option. The Witness option uses a third-party server to monitor the health and connectivity of both SRDF/Metro arrays and to arbitrate in case of a failure. The Array Witness option uses a third array to store configuration information and to arbitrate in case of a failure. However, the Array Witness option does not monitor the health and connectivity of both SRDF/Metro arrays, and it requires manual intervention to resume SRDF/Metro replication after a failure.

정답: 
Explanation:
SRDF device used for Concurrent SRDF environments = R21 SRDF device used for SRDF/Star environments = R11 SRDF device used for Cascaded SRDF environments = R22
A dual personality SRDF device is a device that can act as both an R1 and an R2 device in different SRDF configurations. There are three types of dual personality SRDF devices: R21, R11, and R22.
An R21 device is an R2 device that is paired with another R1 device in a different SRDF group. This allows the R21 device to receive updates from the primary site and send updates to the secondary site. An R21 device is used for Concurrent SRDF environments, which provide simultaneous disaster recovery and data migration capabilities. For example, an R21 device can be used to migrate data from one array to another while maintaining a synchronous copy of the data on a third array.1
An R11 device is an R1 device that is paired with another R1 device in a different SRDF group. This allows the R11 device to receive updates from the primary site and send updates to the tertiary site. An R11 device is used for SRDF/Star environments, which provide three-site disaster recovery capabilities with a single hop between any two sites. For example, an R11 device can be used to create a synchronous copy of the data on a secondary site and an asynchronous copy of the data on a tertiary site.2
An R22 device is an R2 device that is paired with another R2 device in a different SRDF group. This allows the R22 device to receive updates from the secondary site and send updates to the tertiary site. An R22 device is used for Cascaded SRDF environments, which provide three-site disaster recovery capabilities with two hops between the primary and tertiary sites. For example, an R22 device can be used to create an asynchronous copy of the data on a secondary site and another asynchronous copy of the data on a tertiary site.3
Reference:
Dell EMC SRDF Introduction - Dell Technologies Partner Portal Dell EMC PowerMax and VMAX All Flash: SRDF Product Guide Dell EMC PowerMaxOS Performance Guide
정답:
Explanation:
The user has been assigned the RemoteRep role only. The RemoteRep role allows users to create, manage, and delete SRDF device pairs, as well as view array information, masking objects, device information, and RBAC rules2. However, it does not allow users to create and delete SRDF groups, which requires the StorageAdmin role. Therefore, answer C is correct.
A, B, and D are incorrect because they do not match the user’s profile. SecurityAdmin (A) role allows users to manage security settings such as authentication methods, certificates, RBAC rules, and audit logs2. Auditor (B) role allows users to view array information and audit logs only2. LocalRep (D) role allows users to create, manage, and delete TimeFinder SnapVX sessions from a source device2. None of these roles allow users to create and delete SRDF device pairs.
정답:
Explanation:
Data Domain is the only external storage that can be connected to PowerMax using DX emulation. DX emulation is a specialized back-end DA emulation that handles SAN attached disks. DX directors are configured on existing PowerMax front-end Fibre Channel ports and are required to be implemented in pairs for high availability. DX emulation is used to support ProtectPoint technology, which integrates primary storage with Data Domain protection storage to accelerate backup and recovery. Therefore, answer A is correct1.
B, C, and D are incorrect because they are not external storage that can be connected to PowerMax using DX emulation. Unity (B), PowerStore ©, and Compellent (D) are primary storage arrays that do not support ProtectPoint technology or DX emulation.
정답:
Explanation:
When the cache space fills up, I/O will be queued until an empty cache slot is available. This is because PowerMax operates as a cache-centric architecture, where all data is passed through cache before being stored on disk. Cache is used to buffer incoming and outgoing data, as well as to support various functions such as replication and data reduction. When cache is full, the array cannot accept any more data until some cache slots are freed up by flushing data to disk or invalidating stale data. Therefore, answer B is correct.
A, C, and D are incorrect because they do not describe what happens when cache space fills up. I/O will not be serviced at the speed of the destination device (A), as this would bypass the cache and degrade performance. Cache is not permanently flushed © or temporarily disabled (D), as this would result in data loss or corruption.
정답:
Explanation:
A noisy neighbor issue occurs when one or more applications consume more resources than expected, causing performance degradation for other applications. This can affect the SL compliance of a storage group, as the service level defines the expected response time and performance for the applications in that group. If a noisy neighbor consumes too much cache, bandwidth, or CPU cycles, it can cause the SL compliance to drop below the target level. Therefore, answer A is correct.
B, C, and D are incorrect because they are not likely to cause SL compliance impact for a storage group. Queue depth full event (B) is a host-side issue that occurs when the host queue depth is too low or the host I/O rate is too high, causing the host to stop sending I/O requests to the array. Host queue depth setting © is also a host-side parameter that determines how many I/O requests can be queued by the host. Performance thresholds (D) are user-defined values that trigger alerts when certain metrics exceed or fall below the specified levels. None of these factors affect the SL compliance of a storage group on the array.