Aruba Certified Campus Access Associate Exam 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년04월29일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 HP HPE6-A85 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 HPE6-A85 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 60개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
The correct statement when comparing 5 GHz and 6 GHz channels with identical channel widths is that 5 GHz channels travel different distances and provide different throughputs to clients compared to 6 GHz channels. This statement reflects the fact that higher frequency signals tend to have higher attenuation Attenuation is a general term that refers to any reduction in signal strength during transmission over distance or through an object or medium. Higher attenuation means that higher frequency signals have shorter range and lower throughput than lower frequency signals.
Some facts about this statement are:
- 5 GHz channels have lower frequency than 6 GHz channels, which means they have lower attenuation than 6 GHz channels.
- Lower attenuation means that 5 GHz channels can travel longer distances and provide higher throughputs to clients than 6 GHz channels with identical channel widths.
- However, the difference in distance and throughput between 5 GHz and 6 GHz channels may not be significant in indoor environments where there are many obstacles and reflections that affect signal propagation.
- The advantage of using 6 GHz channels over 5 GHz channels is that they offer more spectrum availability, less interference, and more non-overlapping channels than 5 GHz channels.
The other options are not correct because:
- 5 GHz channels travel the same distances and provide different throughputs to clients compared to 6 GHz channels: This option is false because 5 GHz channels do not travel the same distances as 6 GHz channels due to higher attenuation of higher frequency signals.
- 5 GHz channels travel the same distances and provide the same throughputs to clients compared to 6 GHz channels: This option is false because 5 GHz channels do not travel the same distances or provide the same throughputs as 6 GHz channels due to higher attenuation of higher frequency signals.
- 5 GHz channels travel different distances and provide the same throughputs to clients compared to 6 GHz channels: This option is false because 5 GHz channels do not provide the same throughputs as
6 GHz channels due to higher attenuation of higher frequency signals.
References:
https://www.wi-fi.org/discover-wi-fi/wi-fi-certified-6e
https://www.wi-fi.org/file/wi-fi-alliance-spectrum-needs-study
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/wireless-mobility/wireless-lan-wlan/82068-power-levels.html
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/wireless/spectrum-expert-wi-fi/prod_white_paper0900aecd80
정답:
Explanation:
A static route is a route that is manually configured on a router or switch and does not change unless it is modified by an administrator. Static routes are used to specify how traffic should reach specific destinations that are not directly connected to the device or that are not reachable by dynamic routing protocols. In Aruba CX switches, static routes can be configured using the ip route command in global configuration mode. Based on the “show ip route” output on an Aruba CX 8400 switch, the route “10.1 20 0/24, vrf default via 10.1.12.2, [1/0]” is a static route because it has an administrative distance of 1 and a metric of 0, which are typical values for static routes.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Static_routing
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX_10_04/NOSCG/Content/cx-noscg/ip-routing/static-routes.h
정답:
Explanation:
This configuration script will achieve the task as it follows the guidelines given by the Senior Engineer. It creates VLAN 20 with name Mgmt, adds L3 SVI on VLAN 20 with IP address 10.1.1.10/24, creates LAG 1 with LACP mode active for the uplink, uses VLAN 20 as the native VLAN on the LAG, and ensures that the interfaces are all ON.
References: https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.04/HTML/5200-6790/GUID-8F0E7E8B-0F4

정답: 
Explanation:
- Add certificates to Android devices with the Aruba Onboard Application in the Google Play store that will be used for wireless authentication A) ClearPass Policy Manager
- Authenticate users on corporate-owned Chromebook devices using 802.1X and context gathered from the network devices that they log into B) Cloud Authentication and Policy
- Leverage unbound Mum Pre-Shared Keys (MPSK) managed by Aruoa Central to the end-users and client devices B) Cloud Authentication and Policy
- Validate devices exist in a Mobile Device Management (MDM) database before authenticating BYOD users with corporate Active Directory using certificates A) ClearPass Policy Manager
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ClearPass/6.11/PolicyManager/Content/CPPM_UserGuide/About%2
https://www.arubanetworks.com/products/security/network-access-control/
정답:
Explanation:
Profiling is a feature that allows Aruba switches to automatically identify and classify devices connected to them based on various attributes such as MAC address, DHCP options, LLDP information, etc. Profiling can be used to dynamically set the PoE priority on a switch port based on the device type and power requirements. For example, an IP camera may have a higher PoE priority than a printer or a PC. Profiling can also be used to apply other configuration settings such as VLANs, ACLs, QoS, etc. based on the device profile. References: https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ArubaOS_86_Web_Help/Content/arubaos-solutions/1-ov
정답:
Explanation:
Aruba Central allows you to create device configuration groups that define common settings for devices within each group. You can create different types of groups depending on your network requirements and management preferences.
Two types of groups that you can define in Aruba Central during group creation are:
- Template group: A template group allows you to create configuration templates using variables and expressions that can be applied to multiple devices or device groups. Template groups provide flexibility and scalability for managing large-scale deployments with similar configurations.
- Default group: A default group is automatically created when you add devices to Aruba Central for the first time. The default group contains basic configuration settings that are applied to all devices that are not assigned to any other group. You can modify or delete the default group as needed.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/Central/latest/content/nms/device-groups.htm
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/Central/latest/content/nms/template-groups.htm
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/Central/latest/content/nms/default-group.htm
정답:
Explanation:
The ideal access switch for a large hospital with distribution racks of over 400 ports in a single VSF stack is the CX 6300.
This switch provides the following benefits:
- The CX 6300 supports up to 48 ports per switch and up to 10 switches per VSF stack, allowing for a total of 480 ports in a single stack. This meets the requirement of having over 400 ports in a single VSF stack.
- The CX 6300 supports high-performance switching with up to 960 Gbps of switching capacity and up to 714 Mpps of forwarding rate. This meets the requirement of having high throughput and low latency for mobile equipment and patient data.
- The CX 6300 supports advanced features such as dynamic segmentation, policy-based routing, and role-based access control. These features enhance the security and flexibility of the network by applying different policies and roles to different types of devices and users.
- The CX 6300 supports Aruba NetEdit, a network configuration and orchestration tool that simplifies the management and automation of the network. This reduces the complexity and human errors involved in network configuration and maintenance.
The other options are not ideal because:
- OCX 6400: This switch is designed for data center applications and does not support VSF stacking. It also does not support dynamic segmentation or policy-based routing, which are useful for network security and flexibility.
- OCX 6200: This switch is designed for small to medium-sized businesses and does not support VSF stacking. It also has lower switching capacity and forwarding rate than the CX 6300, which may affect the performance of the network.
- OCX 6100: This switch is designed for edge applications and does not support VSF stacking. It also has lower switching capacity and forwarding rate than the CX 6300, which may affect the performance of the network.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/ds/DS_CX6300Series.pdf
https://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/ds/DS_OC6400Series.pdf
https://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/ds/DS_OC6200Series.pdf
https://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/ds/DS_OC6100Series.pdf
정답:
Explanation:
The option that allows you to access the switch and see the boot options available for OS images and ServiceOS is Conductor USB-C console port. This option provides direct access to ServiceOS, which is an operating system that runs on Aruba CX switches independently of AOS-CX Aruba Operating System CX (AOS-CX) is an operating system that runs on Aruba CX switches. ServiceOS provides low-level functions such as booting, firmware upgrades, password recovery, hardware diagnostics, switch stacking, and system recovery.
ServiceOS can be accessed through one of two methods:
- Conductor USB-C console port: This method allows you to connect your PC or laptop to the USB-C console port on any member switch in a VSF stack using a USB-C cable. This method provides direct access to ServiceOS without requiring any configuration or authentication on AOS-CX.
- AOS-CX CLI: This method allows you to access ServiceOS through AOS-CX CLI using SSH or Telnet protocols. This method requires you to configure an IP address on AOS-CX and authenticate with your username and password.
To see the boot options available for OS images and ServiceOS, you need to access ServiceOS through Conductor USB-C console port and enter boot menu command at ServiceOS prompt.
The other options do not allow you to access the switch and see the boot options available for OS images and ServiceOS because:
- Member 2 RJ-45 console port: This option allows you to connect your PC or laptop to the RJ-45 console port on any member switch in a VSF stack using an RJ-45 cable. This option provides direct access to AOS-CX CLI, not ServiceOS.
- Member 2 switch mgmt port: This option allows you to connect your PC or laptop to the switch mgmt port on any member switch in a VSF stack using an Ethernet cable. This option provides indirect access to AOS-CX CLI through SSH or Telnet protocols, not ServiceOS.
- Conductor mgmt port using SSH: This option allows you to connect your PC or laptop to the mgmt port on any member switch in a VSF stack using an Ethernet cable. This option provides indirect access to AOS-CX CLI through SSH protocol, not ServiceOS.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX_10_08/NOSCG/Content/cx-noscg/serviceos/serviceos-over
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX_10_08/NOSCG/Content/cx-noscg/serviceos/access-service
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX_10_08/NOSCG/Content/cx-noscg/serviceos/boot-menu.htm
정답:
Explanation:
OAlOps is a feature of Aruba Central that uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify recommended steps to resolve network health issues and allows you to share detailed information with support personnel. OAlOps provides insights into network performance, root cause analysis, anomaly detection, proactive alerts, and automated remediation actions. OAlOps also integrates with Aruba User Experience Insight (UXI) sensors to measure and improve user experience across wired and wireless networks.
References: https://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/ds/DS_ArubaCentral.pdf
정답:
Explanation:
A frame is the data link layer PDU that encapsulates the network layer PDU (packet) with a header and a trailer that contain information such as source and destination MAC addresses, frame type, error detection, etc. A frame is transmitted over a physical medium such asEthernet, Wi-Fi, etc.
References: https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ArubaOS_86_Web_Help/Content/arubaos-solutions/1-ov
정답:
Explanation:
The command that is used to set a default route to 10.4.5.1 on an Aruba CX switch when in-band management using an SVI is being used is ip route 0.0 0 0/0 10.4.5.1. This command specifies the destination network address (0.0 0 0) and prefix length (/0) and the next-hop address (10.4.5.1) for reaching any network that is not directly connected to the switch. The default route applies to the default VRF Virtual Routing and Forwarding. VRF is a technology that allows multiple instances of a routing table to co-exist within the same router at the same time. VRFs are typically used to segment network traffic for security, privacy, or administrative purposes., which is used for in-band management traffic that goes through an SVI Switch Virtual Interface. SVI is a virtual interface on a switch that allows the switch to route packets between different VLANs on the same switch or different switches that are connected by a trunk link. An SVI is associated with a VLAN and has an IP address and subnet mask assigned to it12. References:
1 https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10_08/HTML/ip_route_4100i-6000-6100-6200/Content/Ch
2 https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10_08/HTML/ip_route_4100i-6000-6100-6200/Content/Ch
정답:
Explanation:
The option that fulfills the requirements is to create individual SSIDs with unique PSK for each loT class, using 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz band.
This option provides the following benefits:
- Each loT class has a unique PSK that can be used to apply a different security policy as a role. This enhances the security and flexibility of the WLAN network.
- Individual SSIDs allow for better isolation and management of different loT classes. This improves the performance and scalability of the WLAN network.
- Using both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands allows for backward compatibility with loT devices that operate only with 802.11b, which uses the 2.4 GHz band1. It also allows for higher throughput and less interference for loT devices that support 802.11a, 802.11g, 802.11n, or 802.11ac, which use the 5 GHz band2.
The other options do not fulfill the requirements because:
- Single SSID with MPSK for each loT class using 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands: This option does not support loT devices that operate only with 802.11b, which uses the 2.4 GHz band1. It also does not optimize the performance of the WLAN network, as a single SSID may cause co-channel interference and congestion among different loT classes.
![]()
- Single SSID with MPSK for each loT class using 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands: This option does not optimize the performance of the WLAN network, as a single SSID may cause co-channel interference and congestion among different loT classes.
- Individual SSIDs with unique PSK for each loT class, using 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands: This option does not support loT devices that operate only with 802.11b, which uses the 2.4 GHz band1.
References:
1 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.11b-1999
2 https://www.lifewire.com/wireless-standards-802-11a-802-11b-g-n-and-802-11ac-816553
정답:
Explanation:
The Alerts and Events dashboard displays all types of alerts and events generated for events pertaining to device provisioning, configuration, and user management. You can use the Config icon to configure alerts and notifications for different alert categories and severities1. You can also view the alerts and events in the List view and Summary view2.
References:
1 https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/central/latest/content/nms/alerts/configuring-alerts.htm
2 https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/central/latest/content/nms/alerts/viewing-alerts.htm
정답:
Explanation:
If the AP has internet access but does not receive its configuration from Aruba Central, one possible reason is that the AP does not have a license assigned in Aruba Central. A license is required for each AP to be managed by Aruba Central.
References: https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/Central/2.5.2-GA/HTML_frameset.htm#GUID-8F0E7E8
정답: 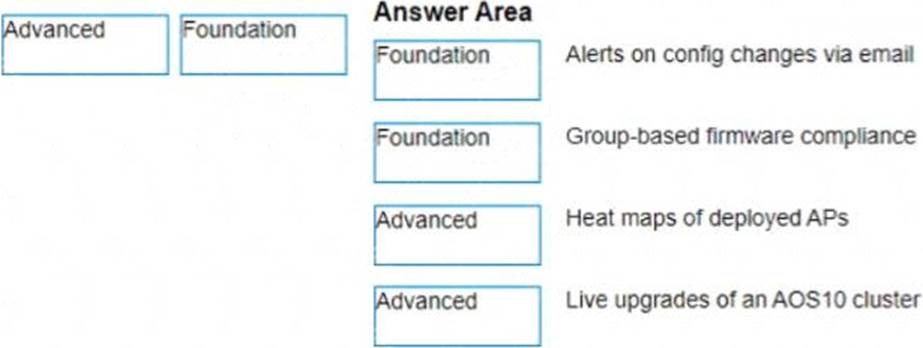
Explanation:
a) Alerts on config changes via email - Foundation
b) Group-based firmware compliance - Foundation
c) Heat maps of deployed APs - Advanced
d) Live upgrades of an AOS10 cluster - Advanced
According to the Aruba Central Licensing Guide1, the Foundation License provides basic device management features such as configuration, monitoring, alerts, reports, firmware management, etc. The Advanced License provides additional features such as AI insights, WLAN services, NetConductor Fabric, heat maps, live upgrades, etc.
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/central/2.5.3/content/pdfs/licensing-guide.pdf