Aruba Certified Campus Access Professional Exam 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년03월22일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 HP HPE7-A01 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 HPE7-A01 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 77개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) is a technology that can minimize client latency in a high-density environment by eliminating contention overhead by dedicating subcarriers to clients. OFDMA allows multiple clients to transmit simultaneously on different subcarriers within the same channel, reducing contention and increasing efficiency. MU-MIMO (Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output) is a technology that allows multiple clients to transmit simultaneously on different spatial streams within the same channel, but it does not eliminate contention overhead.
QWMM (Quality of Service Wireless Multimedia) is a technology that prioritizes traffic based on four access categories, but it does not eliminate contention overhead. Channel Bonding is a technology that combines two adjacent channels into one wider channel, increasing bandwidth but not eliminating contention overhead.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/ds/DS_AP510Series.pdf
https://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/wp/WP_WiFi6.pdf
정답:
Explanation:
A session-based ACL is applied to traffic entering or leaving a port or VLAN based on the direction of the session initiation. To allow ping from any wired station to wireless clients but not vice versa, a session-based ACL should be used to deny icmp echo traffic from any source to any destination, and then permit icmp echo-reply traffic from any source to user destination. The user role represents wireless clients in AOS 10.
References:
https://techhub.hpe.com/eginfolib/Aruba/OS-CX_10.04/5200-6692/GUID-BD3E0A5F-FE4C-4B9B-BE1D-FE7D
https://techhub.hpe.com/eginfolib/networking/docs/arubaos-switch/security/GUID-EA0A5B3C-FE4C-4B9B-BE



정답:
Explanation:
Option C is the correct configuration to ensure that APs will work properly. It uses the ap command to configure a port profile for APs with VLAN 100 as the native VLAN and VLAN 200 and 300 as tagged VLANs. It also enables LLDP on the ports to discover the APs and assign them to the port profile automatically. The other options are incorrect because they either do not use the ap command, do not enable LLDP, or do not configure the VLANs correctly.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX_10_08/UG/bk01-ch02.html
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX_10_08/UG/bk01-ch03.html
정답:
Explanation:
The calculated Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) for AP1 is 30 dBm. EIRP is the product of the transmitter power (in dBm) and the antenna gain (in dBi) minus the cable loss (in dB). For AP1, EIRP = 10 dBm + 9 dBi - 2 dB = 17 dBm. For AP2, EIRP = 11 dBm + 12 dBi - 3 dB = 20 dBm.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ArubaOS_86_Web_Help/Content/arubaos-solutions/wlan-rf/rf-fundam
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ArubaOS_86_Web_Help/Content/arubaos-solutions/wlan-rf/eirp.htm
정답:
Explanation:
To allow ClearPass to perform a CoA and change the access for a wired device, the following steps need to be implemented:
* Confirm that NTP is configured on the switch and ClearPass. NTP is required to synchronize the time between the switch and ClearPass, which is essential for CoA messages to be processed correctly1.
* Configure dynamic authorization on the switch. Dynamic authorization is a feature that enables the switch to accept CoA messages from a RADIUS server and apply them to existing sessions2. Dynamic authorization can be enabled globally or per port on the switch2.
* Optionally, configure dynamic authorization on the switchport. This step is not required, but it can provide more granular control over which ports can accept CoA messages from a RADIUS server2. Bouncing the switchport or using Dynamic Segmentation are not necessary steps for allowing ClearPass to perform a CoA and change the access for a wired device.
References:
1 https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ClearPass/6.7/Aruba_DeployGd_HTML/Content/Aruba%20Controlle
2 https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.04/HTML/5200-6692/GUID-BD3E0A5F-FE4C-4B9B-B
정답:
Explanation:
EVPN-VXLAN is a technology that allows layer-2 communication across layer-3 networks by using Ethernet VPN (EVPN) as a control plane and Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) as a data plane3. EVPN-VXLAN can be used to support legacy applications that communicate at layer-2 across different campuses or data centers that are connected via layer-3. EVPN-VXLAN minimizes flooding by using BGP to distribute MAC addresses and IP addresses of hosts across different VXLAN segments3. EVPN-VXLAN also provides benefits such as loop prevention, load balancing, mobility, and scalability3.
References: https://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/tg/TG_EVPN_VXLAN.pdf
정답:
Explanation:
CoS and DSCP are both methods of marking packets for quality of service (QoS) purposes. QoS is a mechanism that allows network devices to prioritize and differentiate traffic based on certain criteria, such as application type, source, destination, etc. CoS stands for Class of Service and is a 3-bit field in the 802.1Q VLAN tag header. CoS can only be used on Ethernet frames that have a VLAN tag, and it can only be preserved within a single VLAN domain. DSCP stands for Differentiated Services Code Point and is a 6-bit field in the IP header. DSCP can be used on any IP packet, regardless of the underlying layer 2 technology, and it can be preserved throughout the IP packet flow, unless it is modified by intermediate devices.
References:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/qos/configuration/15-mt/qos-15-mt-book/qos-overview.html
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/lan-switching/8021q/17056-741-4.html
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/quality-of-service-qos/qos-packet-marking/10103-dscpvalues.html
정답:
Explanation:
This is the correct statement about what happens when a client attempts to join the network and the WLAN is configured with OWE (Opportunistic Wireless Encryption). OWE is a standard that provides encryption for open networks without requiring any authentication or credentials from the client or the network. OWE uses a Diffie-Hellman key exchange mechanism to establish a secure session between the client and the AP without exchanging any authentication information. The other options are incorrect because they either describe scenarios that require authentication or encryption methods that are not used by OWE.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/wp/WP_WiFi6.pdf
https://www.arubanetworks.com/assets/ds/DS_AP510Series.pdf

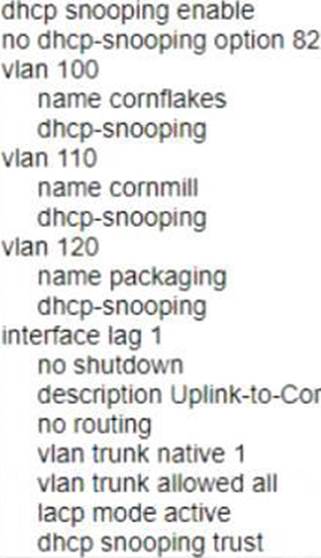

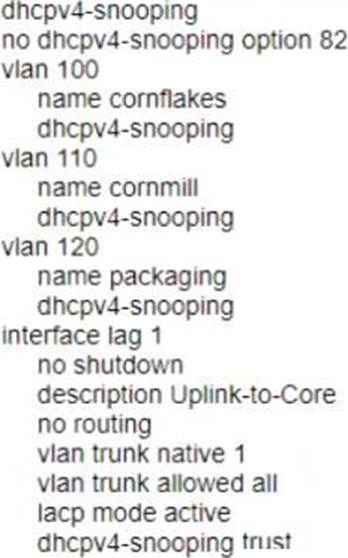
정답:
Explanation:
Option A shows the correct commands to ensure that no rogue DHCP server will impact the network.
The commands include the following steps:
* Enable DHCP snooping on the switch. DHCP snooping is a feature that prevents rogue DHCP servers from offering IP addresses to clients by filtering DHCP messages based on trusted and untrusted ports1.
* Configure VLANs 100, 110, and 120 as DHCP snooping VLANs. This means that DHCP snooping will be applied to these VLANs and any untrusted DHCP messages received on these VLANs will be dropped1.
* Configure LAG 1 as a trusted port for DHCP snooping. This means that any DHCP messages received on LAG 1 will be allowed and not filtered by DHCP snooping. LAG 1 is assumed to be connected to a legitimate DHCP server or a router that relays DHCP requests to a legitimate DHCP server1.
Option B is incorrect because it does not enable DHCP snooping on the switch or configure VLANs 100, 110, and 120 as DHCP snooping VLANs. Option C is incorrect because it does not configure LAG 1 as a trusted port for DHCP snooping. Option D is incorrect because it does not enable DHCP snooping on the switch or configure LAG 1 as a trusted port for DHCP snooping.
References: 1 https://techhub.hpe.com/eginfolib/Aruba/OS-CX_10.04/5200-6692/GUID-BD3E0A5F-FE4C-4B9B-BE1D-FE7
정답:
Explanation:
To create a new OSPF configuration for a separate routing table, you need to create a new OSPF process ID with vrf name. This will create a new OSPF instance that is associated with the specified VRF and its routing table. The other options are incorrect because they either do not create a new OSPF instance or do not associate it with a VRF.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.04/HTML/5200-6728/bk01-ch02.html
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.04/HTML/5200-6728/bk01-ch03.html
정답:
Explanation:
This is the correct definition of Multicast Transmission Optimization in an HPE Aruba wireless network.
Multicast Transmission Optimization is a feature that improves the performance and reliability of multicast traffic by dynamically adjusting the transmission rate based on the highest broadcast rate across all associated clients. This ensures that multicast frames are sent at the optimal rate for each client and reduces retransmissions and packet loss. The other options are incorrect because they either describe different features or use incorrect terms.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ArubaOS_86_Web_Help/Content/arubaos-solutions/multicast/multica
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ArubaOS_86_Web_Help/Content/arubaos-solutions/multicast/multica
정답:
Explanation:
To onboard a new UXI in an existing environment with 802.1X authentication, you need to use the UXI app on your smartphone and connect the UXI via Bluetooth. The UXI app allows you to scan the QR code on the UXI sensor and configure its network settings, such as SSID, password, IP address, etc.
The Bluetooth connection allows you to communicate with the UXI sensor without requiring any network access or cellular connection. The other options are incorrect because they either do not use the UXI app or do not use Bluetooth.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/products/network-management-operations/analytics-monitoring/user-experienc
https://help.centralon-prem.arubanetworks.com/2.5.4/documentation/online_help/content/nms-on-prem/aos-cx/g
정답:
Explanation:
To establish a keepalive connection between two Aruba CX 8325 switches for VSX configuration, you need to use a routed port in custom VRF. A routed port is a physical port that acts as a layer 3 interface and does not belong to any VLAN. A custom VRF is a virtual routing and forwarding instance that provides logical separation of routing tables. By using a routed port in custom VRF, you can isolate the keepalive traffic from other traffic and prevent routing loops or conflicts. The other options are incorrect because they either do not use a routed port or do not use a custom VRF.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.04/HTML/5200-6728/bk01-ch07.html
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/AOS-CX/10.04/HTML/5200-6728/bk01-ch02.html
정답:
Explanation:
Spectrum Monitor is an Aruba AP mode that is sending captured RF data to Aruba Central for waterfall plot.
Spectrum Monitor is a mode that allows an AP to scan all channels in both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands and collect information about the RF environment, such as interference sources, noise floor, channel utilization, etc. The AP then sends this data to Aruba Central, which is a cloud-based network management platform that can display the data in various formats, including waterfall plot. Waterfall plot is a graphical representation of the RF spectrum over time, showing the frequency, amplitude, and duration of RF signals. The other options are incorrect because they are either not AP modes or not sending RF data to Aruba Central.
References:
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ArubaOS_86_Web_Help/Content/arubaos-solutions/1-overview/spect
https://www.arubanetworks.com/techdocs/ArubaOS_86_Web_Help/Content/arubaos-solutions/1-overview/water
https://www.arubanetworks.com/products/network-management-operations/aruba-central/
정답:
Explanation:
OSPF is a link-state routing protocol that divides a network into areas. An area is a logical grouping of routers that share the same link-state information. Area 0 is the backbone area that connects all other areas. A transit network is a special network that connects two different areas. A transit network must belong to Area 0 and have at least two OSPF routers attached to it. A transit network allows traffic from one area to pass through another area without changing the area ID.
References:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/7039-1.html https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/13703-8.html