Aruba Certified Campus Access Mobility Expert Written Exam 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년03월22일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 HP HPE7-A07 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 HPE7-A07 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 70개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
In the United States, the operation in the 6GHz band for Wi-Fi devices such as the AP-634 and AP-635 is regulated by the Automated Frequency Coordination (AFC) system, which determines the channels that can be used based on the location. Since the Proof of Concept (POC) was conducted in a different location using AP-635 APs, the allowable channels identified by the AFC service for that location would be different than the channels allowed for the actual deployment location of the AP-634 APs. This would result in a different set of broadcasting channels being available for use in the new warehouse deployment.
정답:
Explanation:
When onboarding devices into a centralized management system, each device can have its individual admin password set during the onboarding process. If this password doesn't match what is expected at the group level in the central management platform, login issues such as the one described can occur.
정답: 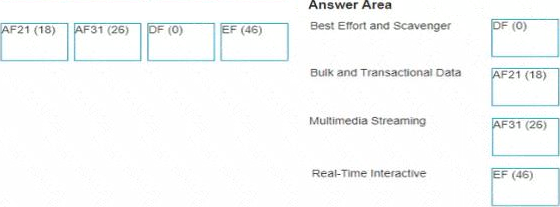
Explanation:
Best Effort and Scavenger =DF (0)
Bulk and Transactional Data =AF21 (18)
Multimedia Streaming =AF31 (26)
Real-Time Interactive =EF (46)
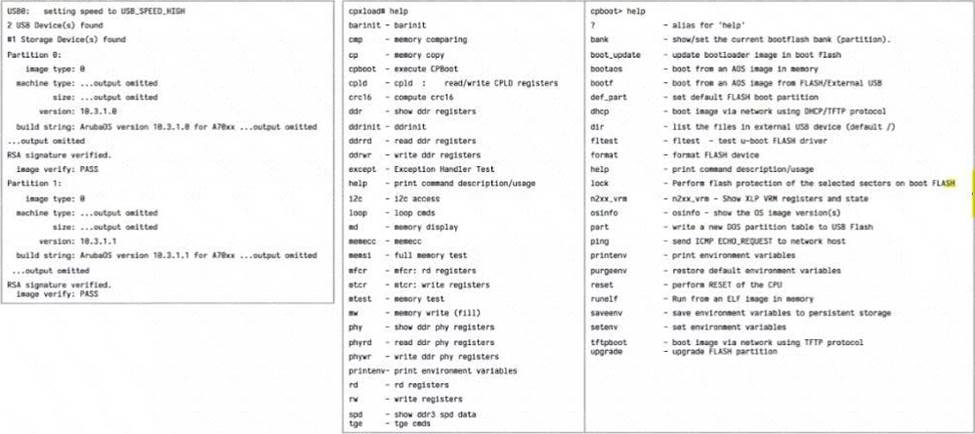

정답: 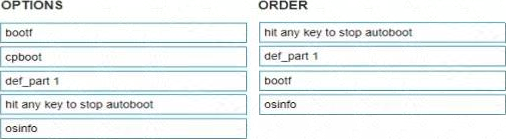
Explanation:
The sequence to return to the previous firmware version after an unsuccessful update would typically be:
hit any key to stop autoboot (This would prevent the system from automatically booting into the current, problematic firmware.)
def_part 1 (This command sets the default boot partition, which is likely where the previous working firmware is located.)
bootf (This command would boot from the specified flash partition, which after the second step, would be the previous firmware.)
osinfo (After the system is booted, this command could be used to confirm the firmware version now running on the gateway.)
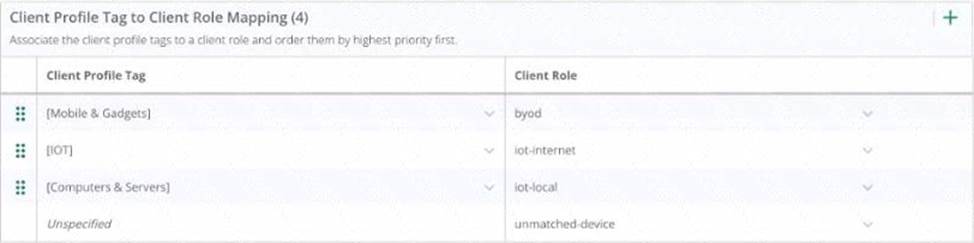
정답:
Explanation:
The configuration shown in the third exhibit details a client role mapping that associates different client profile tags with specific client roles. When a new device, such as an Android phone, connects to the network, it will be profiled and assigned a role based on the mappings defined. If the device does not match any predefined profiles, it would be assigned the "unmatched-device" role. This is under the assumption that default settings are in place and the client does not match the criteria for any of the specific roles like "byod", "iot-internet", or "iot-local". Therefore, an Android phone connecting for the first time and not matching any specific profile tag would be assigned to the "unmatched-device" role.

정답:
Explanation:
Dynamic Multicast Optimization (DMO) is a feature that enhances the delivery of multicast traffic by optimizing the data rate. The before and after optimization images show a significant increase in the data rate, which is a typical result of DMO being configured, as it allows multicast traffic to be transmitted at higher data rates by converting multicast streams into unicast streams for the clients that need them.
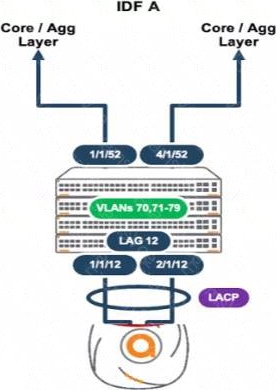
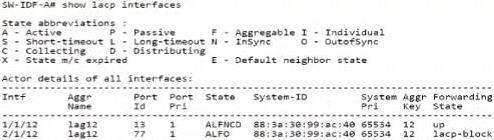
정답:
Explanation:
In an Aruba deployment, if an AP's interfaces show different LACP states, it often indicates a configuration mismatch. If one interface is up and the other is blocked as shown in the output, it’s likely due to both interfaces on the AP being set to LACP active mode, which is a correct setting for establishing an LACP channel with Aruba switches like the CX 6300 series.
정답:
Explanation:
HPE Aruba Networking Central can identify which switch port a rogue AP is connected to by using the switch's MAC address table. The MAC address table contains the associations between MAC addresses and the switch ports to which devices (including APs) are connected. When Aruba Central detects a rogue AP, it can look up the MAC address of the rogue AP in the switch's MAC address table to find the specific switch port it is connected to. This enables network administrators to quickly locate and address the rogue AP issue.
정답:
Explanation:
When configuring Virtual Switching Extension (VSX) in a campus topology for link aggregation across two aggregation switches, it is important to synchronize Multi-Chassis Link Aggregation Group (MC-LAG) interfaces. The command "vsx-sync mclag-interfaces" ensures that the state and configuration of MC-LAG interfaces are synchronized between the two VSX-linked switches,providing consistent link aggregation and preventing any loops or mismatched configurations that might occur if the interfaces were not in sync.

정답:
Explanation:
The fallback role is used as a default role in the absence of a specified role or when an authentication server is not available. Given the scenario, where the test device with MAC address 81:cd:93:13:ab:31 needs to be assigned to "iot-prod" and other devices to "iot-default", and considering there is no external authentication server configured for the test, the appropriate action would be to set a global fallback role that applies to all devices connecting to the network. This ensures that any device that does not match the specific device profile will inherit the "iot-default" role. Since the configuration for a specific MAC address (81:cd:93:xx:xx:xx) to associate with the "iot-prod" role is already in place, setting the fallback role globally accommodates the requirement for other devices.
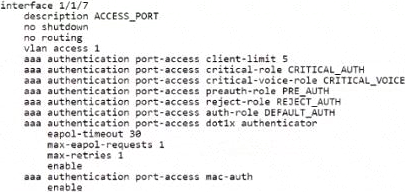
정답:
Explanation:
In the provided configuration for interface 1/1/7, there are roles specified for different scenarios concerning authentication. When a voice client attempts to connect and the RADIUS server is unreachable, the role that is assigned is the one specified as the "critical-voice-role". In this case, the "CRITICAL_VOICE" role is configured to be assigned under such circumstances, ensuring that voice clients receive appropriate network access permissions even when the RADIUS server is not available to authenticate them.
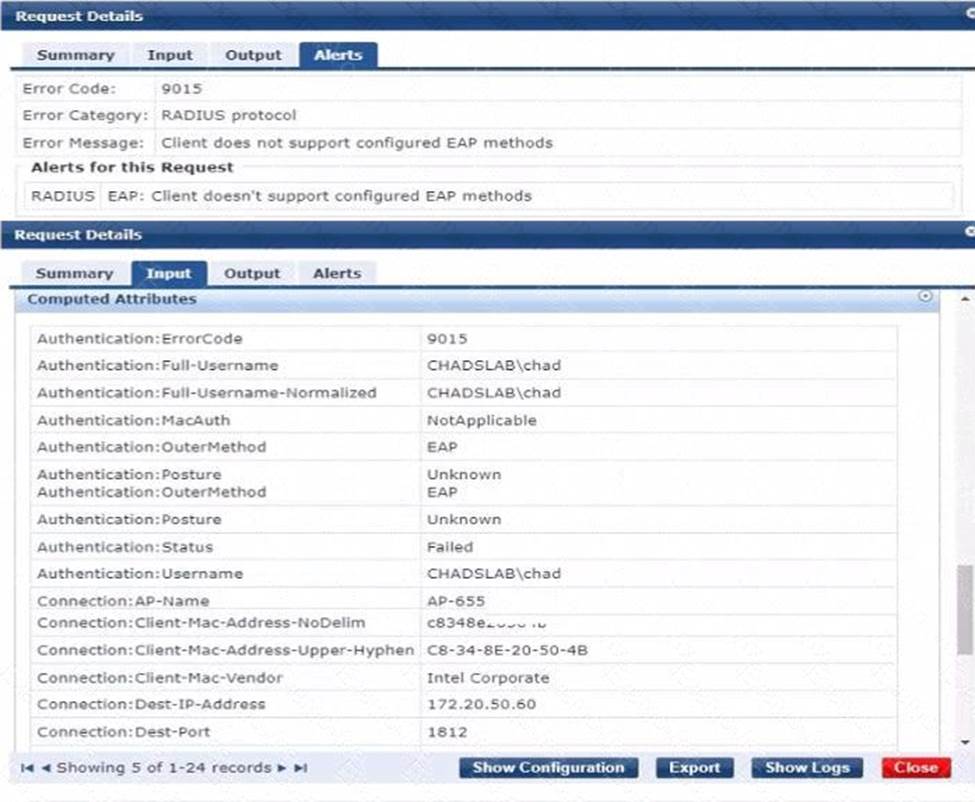
정답:
Explanation:
The issue likely stems from the Windows device not being configured to use TEAP (Tunneled Extensible Authentication Protocol) as specified in the ClearPass configuration. TEAP is an EAP method that encapsulates an inner EAP method for secure authentication. The Windows device must have TEAP enabled and correctly configured in its network settings to authenticate successfully on the network using ClearPass.
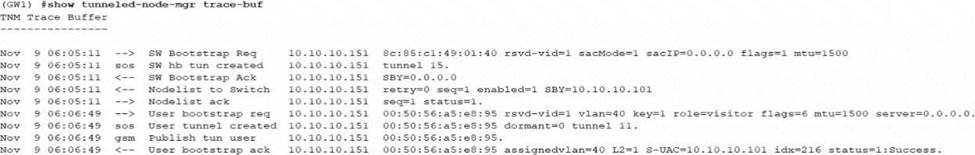
정답:
Explanation:
The CLI output indicates a tunnel creation process, where "SW hw tun created" refers to the switch hardware tunnel being created. The line mentioning "BYP-10.10.10.101 -> SW hw tun created to 10.10.10.151 tunnel 15." implies that a tunnel was established to the secondary tunnel endpoint with the IP address 10.10.10.151. This is a common configuration for User-Based Tunneling (UBT) setups where traffic is tunneled to a specific endpoint.
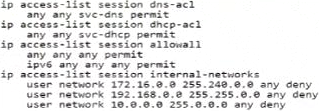

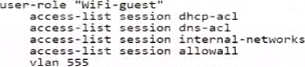

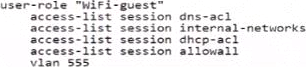
정답:
Explanation:
Based on the criteria provided for wireless guest users, the correct user role configuration must allow internet access, only allow access to public DNS servers, deny access to all internal networks except for any DHCP server, and place the Wi-Fi guests on VLAN 555. The ACLs must permit services necessary for basic internet access (such as DNS and DHCP) and block access to internal networks.
Option A satisfies these criteria with the following configurations:
user-role "WiFi-guest":
This defines the role for Wi-Fi guests.
access-list session dhcp-acl: This applies the access list that likely permits DHCP, which is necessary for guests to obtain an IP address.
access-list session dns-acl: This applies the DNS access list, which likely restricts guests to using public DNS servers.
access-list session internal-networks: This applies the internal networks access list, which denies access to internal networks.
vlan 555: This sets the VLAN for Wi-Fi guests to 555.
Options B, C, and D are incorrect because they includeaccess-list session allowallwhich would permit all traffic, contradicting the requirement to deny access to all internal networks.
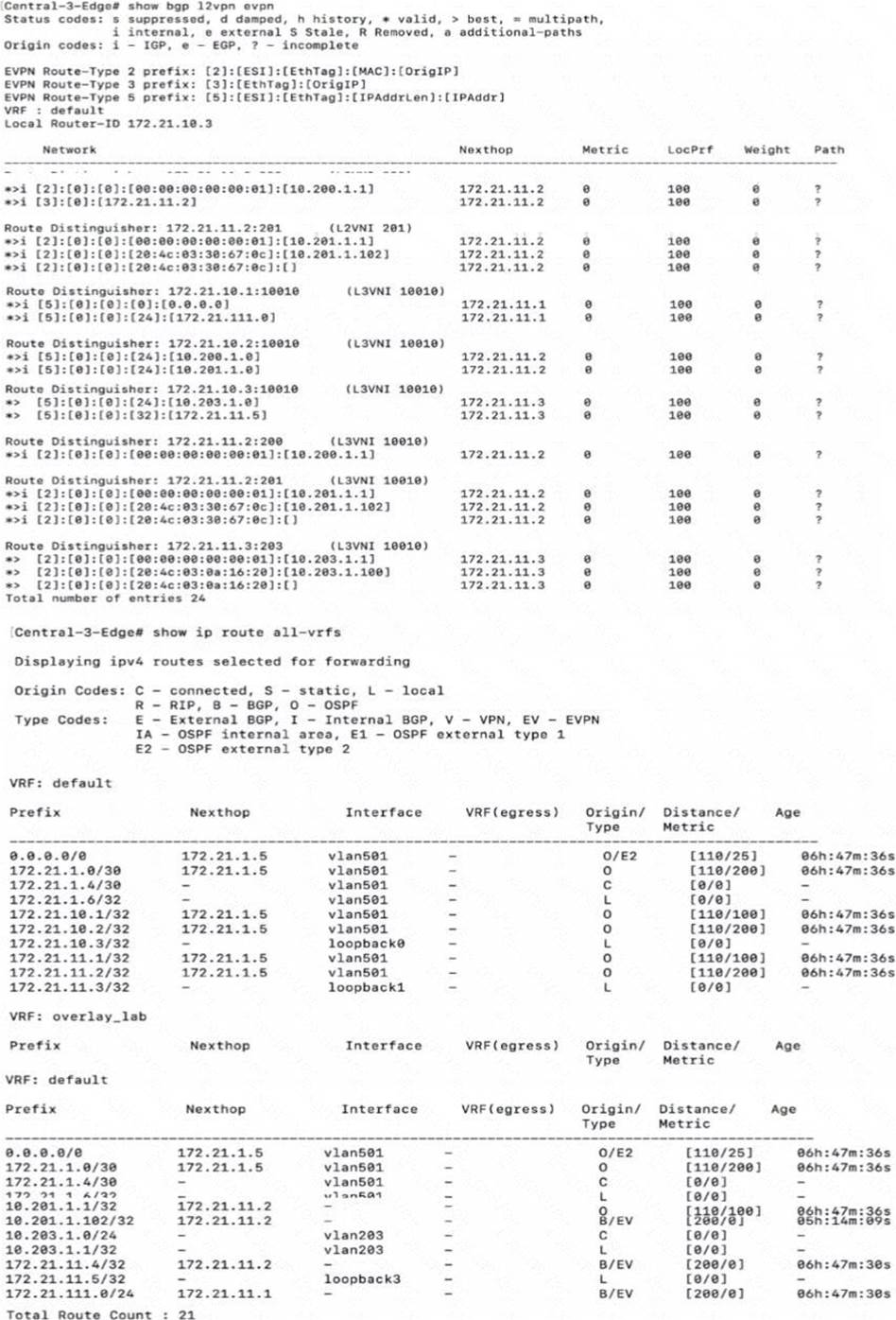
정답:
Explanation:
The CLI output provided shows routing information from a CX 6300 switch. The output under "VRF: default" shows various IP routes, including a route for 10.203.1.100/32 with a next hop of 172.21.11.2. This indicates that the route to the client with IP address 10.203.1.100 is known in the network and is reachable via another device in the fabric, which has the loopback IP address 172.21.11.2. Since the route is present in the routing table, it means that the client is known and active within the fabric network.