Commercial Negotiation 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년03월23일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 CIPS L4M5 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 L4M5 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 162개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
Essential goods andservices such as electricity, fuel, basic food stuffs, commuter transport and habitual products such as tobacco, alcohol and sugar-based drinks are often sited as facing a relatively inelastic demand curve. This means when the price goes up, the quantity demanded does not decrease very much and so they are often the target of government taxation.
LO2, AC 2.2
정답:
Explanation:
Contribution = Price - Variable cost Break-evenpoint (volume) = Fixed cost/Contribution
정답:
Explanation:
Understanding where and with whom your supplier spends their money, or understanding the 'cost breakdowns' or 'price build-up' of the goods andservices you purchase from the supplier, will help you know
where and when they can offer price concessions.
Cost information can be expressed with more impact through graphs that can be created using Excel and PowerPoint or other softwares. There are two commonly used models known as 'spend waterfall'
and 'spend tree'. Spend waterfall shows the build-up of costs, while the spend tree shows all the spends that an organisation makes.
There is no graph known as 'spend candlesticks'. Candlestick chart is astyle of financial chart used to describe price movements of a security, derivative, or currency.
The aggregate expenditure model is a method of calculating GDP. The aggregate expenditure model focuses on the relationships between production (GDP) and planned spending: GDP = planned
spending = consumption + investment + government purchases + net exports.
정답:
Explanation:
In 1983, Peter Kraljic devised a means to segment the supplier base in the article in HBR. In this, heargued that supply items should be mapped against two key dimensions: risk and profitability.
Risk relates to the likelihood for an unexpected event in the supply chains to disrupt operations. For instance, in important areas of spend, such as tire suppliers for an automotive are business critical, and should a disruption occur, the auto company is likely itself to face substantial problems.
Profitability describes the impact of a supply item upon the bottom line. For certain areas of spend, such as stationery, supplies have only a negligible effect on profits. In other categories, a single source of supply can make or break a business.
Putting these two dimensions together yields a classic two-by-two matrix.
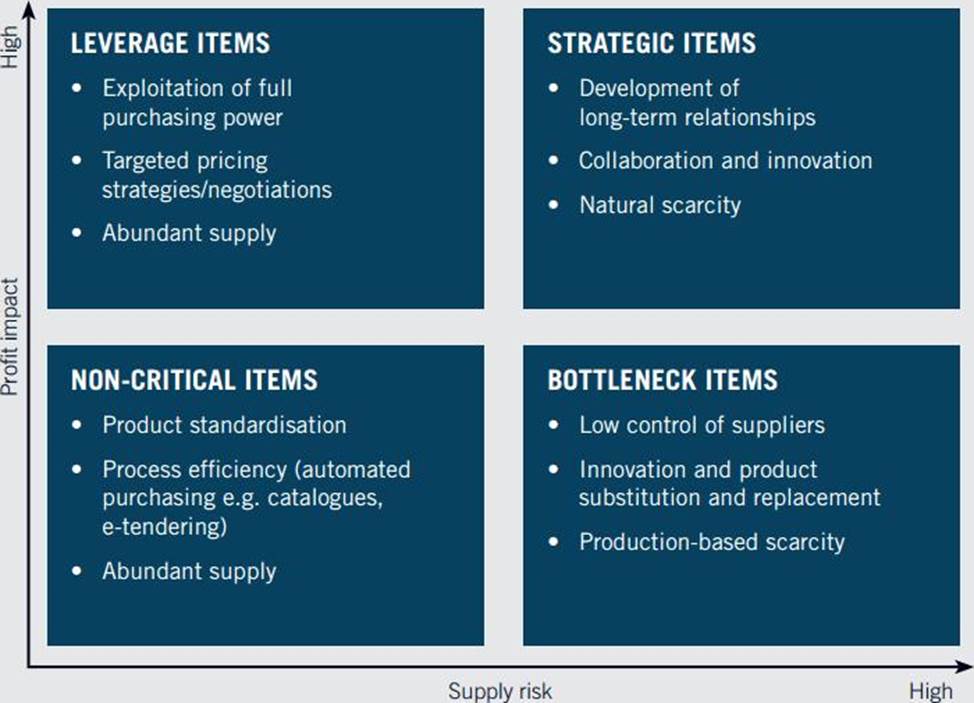
Diagram
Description automatically generated
Source: Peter Kraljic, HBR
Reference:
- CIPS study guide page 63-73
- What Is The Kraljic Matrix? (forbes.com) LO 1, AC 1.4
정답:
Explanation:
Fixed costs (FC) are costs that do not vary with volume. To an airline once aircraft are purchased, flight crews trained and departures scheduled, costs are disproportionately fixed.
Variable costs (VC) are those which vary with the amount produced. Fuel, catering services
and marketing are examples of variable.
LO 2, AC 2.1
정답:
Explanation:
Legitimate power comes from the belief that a person has the formal right to make demands, and to expect others to be compliant and obedient. Legitimate power comes from rules, formal authority, organisation rank, staff grade or official position held. In commercial negotiation, legitimate power can be demonstrated by job title and rank. LO 1, AC 1.3
정답:
Explanation:
There are 5 key phases of negotiation:
The opening phase: confirm understanding and get the issue on the table
The testing phase: check assumption and confirm understanding The proposing phase: asking 'if'
The bargaining phase: using tradeables
The agreement and closing phase
The testing could take the form of questions following a presentation by either side or questions on a tender or proposal document received by the buyer from the potential supplier. The testing phase is necessary to confirm that your approach and objectives are appropriate for the negotiation situation you now find yourself in. Careful listening, observation and interpretation of TOP's responses may give indication of the following: Areas where TOP is willing and unwilling to make concessions What factors or issues TOP places a high value on
If there are any non-commercial or emotional factors that may be pertinent TOP's underlying interests - why they are taking the positionthey are.
정답:
Explanation:
At the first stage of CIPS Procurement and Supply Cycle (Understand need and develop a high-level specification), procurement professional mainly negotiate with internal stakeholders. They have a duty toproportionately and constructively challenge specification if there's genuine doubt over the need or how the need is expressed. This is called demand management. Their first duty is to the organisation's treasury, not to functional managers. Demand management including: negotiation/challenge between procurement and internal stakeholders over the need/requirement/specification. Remember that in any process or product, the greatest opportunity for cost reduction is at the design stage.
정답:
Explanation:
Collaborating is both assertive and cooperative. When collaborating, an individual attempts
to work with the other person to find a solution that fully satisfies the concerns of both. It involves digging into an issue to identify the underlying concerns of the two individuals and to find an alternative that meets both sets of concerns. Collaborating between two persons might take the form of exploring a disagreement to learn from each other’s insights, resolving some condition that would otherwise have them competing for resources, or confronting and trying to find a creative solution to an interpersonal problem.
정답:
Explanation:
There are several pricing strategies used by suppliers:
Cost-plus pricing C Total variable + Fixed cost + profit
Premium pricing C based on branding. Supplier determines to charge a very high price, notconnected with cost structures, usually based on its reputation and/or the perception that the product/service is of
a superior quality. This strategy typically found in the early part of the product life cycle/when demand exceeds supply.
Penetration pricing - Supplier attempts to enter a new market or extend its share in an established one. It is characterised by price reductions to increase volume, followed by steady price increases; may
even be loss leading at start (no profit made) Marginal cost pricing C covers only variable cost
Market pricing C suppliers prices in line with what the market is willing to pay
정답:
Explanation:
Integrative approach to negotiation used when the interested parties are attempting to create more of something of value to share, also known as collaborative approach or win-win. Integrative, interest-based negotiation can facilitate constructive, positive relationship and establishes contracts between parties on a foundation of goodwill. In integrative bargaining, both parties seek to 'expand the pie' by creating more value for both the buyer and the seller. Integrative negotiation ‘shares thepie’ and is interest rather than positional based.
In distributive bargaining, the focus is on claiming value and getting as much of the pie as parties can.
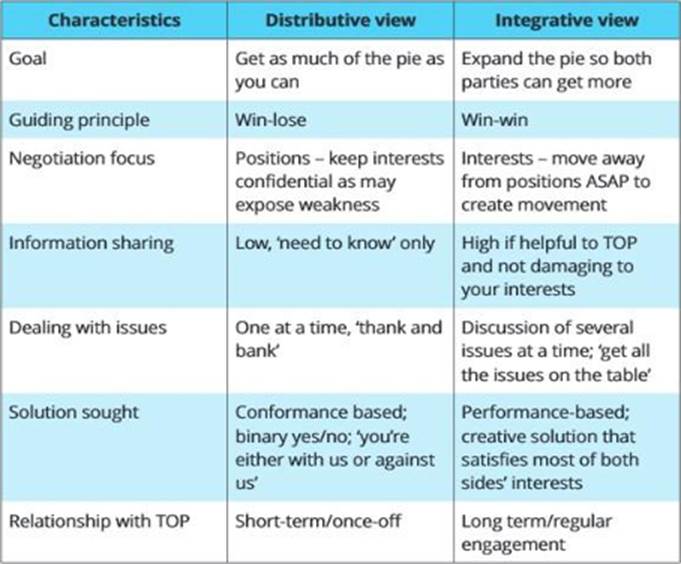
Table
Description automatically generated
LO 1, AC 1.2
정답:
Explanation:
Monopolies exist in many markets in real life for very different reasons:
Ownership of a Key Resource: When one company exerts sole control over a resource that is necessary for the production of a specific product, the market may become a monopoly. For example, the only medication deemed acceptable to treat a disease comes from a particular ingredient X, and knowledge of this ingredient X is owned by a single family owned company. The company can, therefore, be saidto have a monopoly over ingredient X that is needed to cure the disease because it is the only company that can produce a product deemed acceptable.
Government Franchise: In certain instances, a monopoly may be explicitly created by the government if it grants a single company, whether private or government-owned, the right to conduct business in a particular market. For example, when a national railways transportation service is created by the government, in most cases they are granted a monopoly on the operation of passenger trains in the country. As a result, other firms are only able to offer passenger train services with the cooperation and/or permission of the government-owned provider.
Intellectual Property Protection: Extending intellectual property protection to a company in the form of patents and copyrights is yet another way in which monopolies are created. When a government does this, it is in fact giving a single company an exclusive right to provide a particular product / service to the market. Patents and copyrights work in providing owners of intellectual property with the right to act as an exclusive provider of a new product for a specific length of time. This creates a temporary monopoly in the market with regards to new products and services.
Natural Monopoly: A market may also become a monopoly simply because it may be more cost-effective for one company to serve the whole market than to have several smaller firms in competition with one another. A company with virtually unlimited economies of scale is referred to as a natural monopoly. Such firms become monopolies due to their position and size, which makes it impossible for new entrants in the market to compete price-wise. Natural monopolies are common in industries with high fixed costs and low marginal costs of operation such as providers of television, telephone, and internet services.
In this question, 'A single firm is very large' is not enough to tell whether this market is monopolistic.
정답:
Explanation:
Supplier conditioning is the process of influencing a supplier or suppliers to behave in a certain way, or to accept certain circumstances. Within a negotiation, the buyer needs to make sure that the supplier has a number of messages in mind, about the outcomes that the buyer needs to achieve and about the shared sense of purpose that buying organisation has in achieving these outcomes.
Supplier appraisal is a process of evaluating a supplier's ability to carry out a contract in term of quality, delivery, price and other contributing factors.
Supplier positioning is the process of classifying spend with a supplier in terms of the profit potential and supply risk and assists in prioritising categories of spend and developing the rightstrategy.
Supplier selection is the process of selecting a supplier to acquire the necessary materials to support the outputs of organisations. Selection of the best and/or the most suitable suppliers is based on assessing supplier capabilities (Shih et al., 2004).
정답:
Explanation:
Using webcams in a web conference means you are able to communicate both verbally and non verbally.
Over the phone, you cannot see TOP, the only cue/signal you have regarding their mood, interest and attitude is person's voice, intonation andany delay.
A teleconference is a telephone meeting among two or more participants involving technology more sophisticated than a simple two-way phone connection.
In-person meeting requires you team and TOP to be in the same place at the same time. LO 2, AC 2.4
정답:
Explanation:
According to Thomas-Kilmann conflict model instrument, there are 5 conflict management styles:
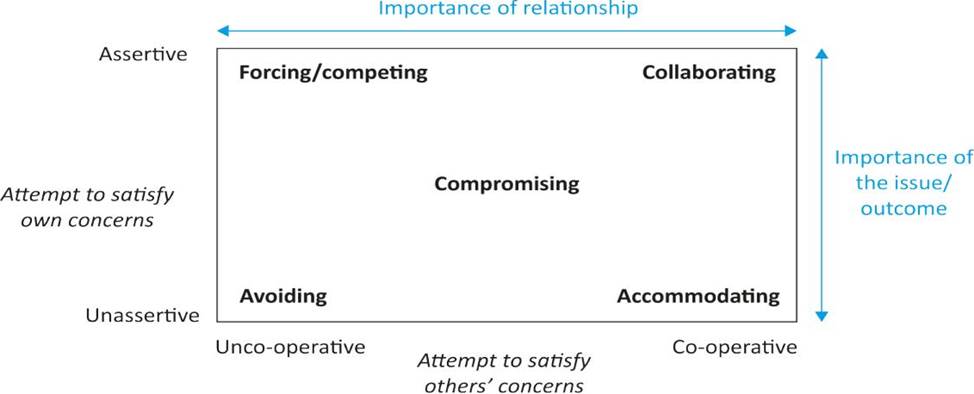
Graphical user interface, text, application, email
Description automatically generated
In this scenario, the buyer's bargaining power is stronger than suppliers', and the relationship is transactional. Therefore, to get the most preferable outcome, the procurement professional can take an assertive approach, while he doesn't need to co-operate closely with these suppliers. Competing will be the most appropriate approach to negotiation in this scenario so that the buying organisation can get a better deal.