Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiAuthenticator 6.4 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년04월10일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 Fortinet NSE6_FAC-6.4 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 NSE6_FAC-6.4 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 47개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
A SAML metadata file can be used to import the required IDP configuration for SAML service provider mode. A SAML metadata file is an XML file that contains information about the identity provider (IDP) and the service provider (SP), such as their entity IDs, endpoints, certificates, and attributes. By importing a SAML metadata file from the IDP, FortiAuthenticator can automatically configure the necessary settings for SAML service provider mode.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/saml-service-provider#saml-metadata
정답:
Explanation:
Two features of FortiAuthenticator that are used for EAP deployment are certificate authority and RADIUS server. Certificate authority allows FortiAuthenticator to issue and manage digital certificates for EAP methods that require certificate-based authentication, such as EAP-TLS or PEAP-EAP-TLS. RADIUS server allows FortiAuthenticator to act as an authentication server for EAP methods that use RADIUS as a transport protocol, such as EAP-GTC or PEAP-MSCHAPV2.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/wireless-802-1x-authentication
정답:
Explanation:
To monitor FortiAuthenticator system information and receive FortiAuthenticator traps through SNMP, two configurations must be performed after enabling SNMP access on the FortiAuthenticator interface:
Set the thresholds to trigger SNMP traps for various system events, such as CPU usage, disk usage, memory usage, or temperature.
Upload management information base (MIB) files to SNMP server to enable the server to interpret the SNMP traps sent by FortiAuthenticator.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/system-settings#snmp
정답:
Explanation:
PEAP is known as the outer authentication method because it establishes a secure tunnel between the client and the server using TLS. The inner authentication method, such as EAP-GTC, EAP-TLS, or MSCHAPV2, is then used to authenticate the client within the tunnel.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/wireless-802-1x-authentication#peap
정답:
Explanation:
FortiAuthenticator can create two types of digital certificates: user certificates and local service certificates. User certificates are issued to users or devices for authentication purposes, such as VPN, wireless, or web access. Local service certificates are issued to FortiAuthenticator itself for securing its own services, such as HTTPS, RADIUS, or LDAP.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/certificate-management#certificate-types
정답:
Explanation:
SP-initiated SSO SAML packet flow for a host without a SAML assertion is as follows:
Principal contacts service provider, requesting access to a protected resource.
Service provider redirects principal to identity provider, sending a SAML authentication request.
Principal authenticates with identity provider using their credentials.
After successful authentication, identity provider redirects principal back to service provider, sending a SAML response with a SAML assertion containing the principal’s attributes.
Service provider validates the SAML response and assertion, and grants access to the principal.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/saml-service-provider#sp-initiated-sso
정답:
Explanation:
Network HSM is a feature that allows FortiAuthenticator to keep local CA cryptographic keys stored in a central location. HSM stands for Hardware Security Module, which is a physical device that provides secure storage and generation of cryptographic keys. Network HSM allows FortiAuthenticator to use an external HSM device to store and manage the private keys of its local CAs, instead of storing them locally on the FortiAuthenticator device.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/certificate-management#network-hsm
정답:
Explanation:
An OCSP responder URL in an end-entity certificate is used to designate a server for certificate status checking. OCSP stands for Online Certificate Status Protocol, which is a method of verifying whether a certificate is valid or revoked in real time. An OCSP responder is a server that responds to OCSP requests from clients with the status of the certificate in question. The OCSP responder URL in an end-entity certificate points to the location of the OCSP responder that can provide the status of that certificate.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/certificate-management#ocsp-responder
정답:
Explanation:
One possible cause of the issue is time drift between FortiAuthenticator and hardware tokens. Time drift occurs when the internal clocks of FortiAuthenticator and hardware tokens are not synchronized. This can result in mismatched one-time passwords (OTPs) generated by the hardware tokens and expected by FortiAuthenticator. To prevent this issue, FortiAuthenticator provides a time drift tolerance option that allows a certain number of seconds of difference between the clocks.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/two-factor-authentication#time-drift-tolerance
정답:
Explanation:
When deploying FortiAuthenticator for portal services, such as guest portal, sponsor portal, user portal or FortiToken activation portal, the network configuration must allow specific ports to be open between FortiAuthenticator and the authentication clients.
These ports are:
TCP 80 for HTTP access
TCP 443 for HTTPS access
TCP 389 for LDAP access
TCP 636 for LDAPS access
UDP 1812 for RADIUS authentication
UDP 1813 for RADIUS accounting
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/portal-services#network-configuration
정답:
Explanation:
Adaptive Authentication is a feature that allows administrators to bypass the need for two-factor authentication for users accessing from specific secured networks. Adaptive Authentication uses geolocation information from IP addresses to determine whether a user is accessing from a trusted network or not. If the user is accessing from a trusted network, FortiAuthenticator can skip the second factor of authentication and grant access based on the first factor only.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/authentication-policies#adaptive-authentication
정답:
Explanation:
Realms are a way to delegate user accounts, user groups and permissions per domain when they are authenticating on a single FortiAuthenticator device. A realm is a logical grouping of users and groups based on a common attribute, such as a domain name or an IP address range. Realms allow administrators to apply different authentication policies and settings to different groups of users based on their realm membership.
Reference: https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/user-management#realms
정답:
Explanation:
Guest accounts are associated with the sponsor that creates the guest account. A sponsor is a user who has permission to create and manage guest accounts on behalf of other users3. A sponsor can create guest accounts using the sponsor portal or the REST API3. The sponsor’s username is recorded as a field in the guest account’s profile3.
Reference: 3 https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/guest-management#sponsors
정답:
Explanation:
FortiAuthenticator can help facilitate the process of replacing an existing RADIUS server by enabling learning mode in the RADIUS server configuration. This allows FortiAuthenticator to learn user credentials from the existing RADIUS server and store them locally for future authentication requests2. This way, FortiAuthenticator can gradually take over the role of the RADIUS server without disrupting the user experience.
Reference: 2 https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/radius-service#learning-mode
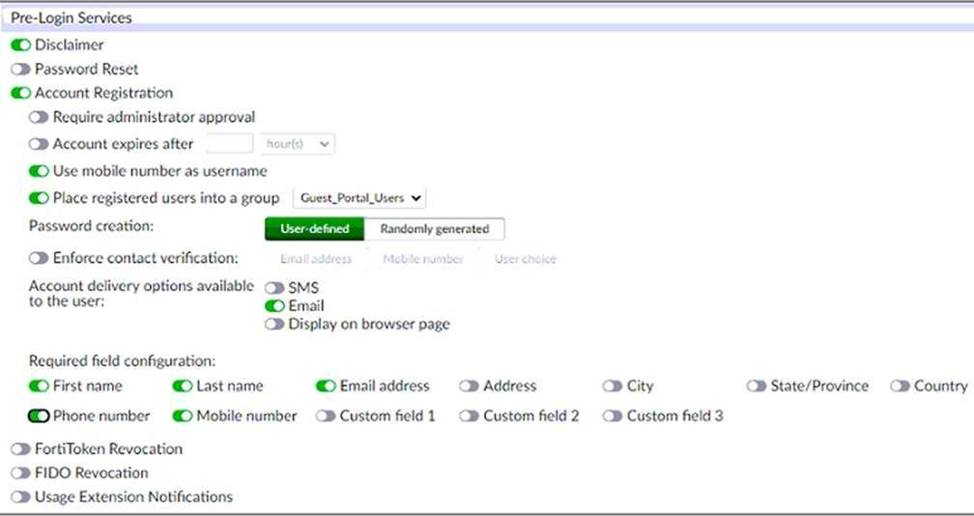
정답:
Explanation:
The screenshot shows that the account registration feature is enabled for the guest portal and that the guest group is set to Guest_Portal_Users. This means that all guest accounts created using this feature will be placed under that group1. The screenshot also shows that email validation is enabled for the guest portal and that the email validation link expires after 24 hours. This means that all accounts registered through the guest portal must be validated through email within that time frame1.
Reference: 1 https://docs.fortinet.com/document/fortiauthenticator/6.4.0/administration-guide/906179/guest-management#account-registration