Fortinet NSE 6 - FortiAnalyzer 7.2 Administrator 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년04월10일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 Fortinet NSE6_FAZ-7.2 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 NSE6_FAZ-7.2 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 80개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
정답:
Explanation:
In aggregation mode, FortiAnalyzer stores logs received from devices and forwards them at a specified time each day to avoid duplication. It is specifically designed to work between two FortiAnalyzer units and does not support syslog or CEF servers. Additionally, aggregation mode configurations are limited to CLI commands log-forward and log-forward-service.
Reference: FortiAnalyzer 7.2 Administrator Guide, "Aggregation" and "CLI Commands for Aggregation Mode" sections.
정답:
Explanation:
To send reports from FortiAnalyzer to an external server, you must configure the output profile. This involves specifying the method (FTP, SFTP, or SCP), server IP, username, password, and the directory where the report will be saved. Additionally, you have the option to delete the report after it has been uploaded to the server.
Reference: FortiAnalyzer 7.2 Administrator Guide, "Enable uploading of generated reports to a server" section.
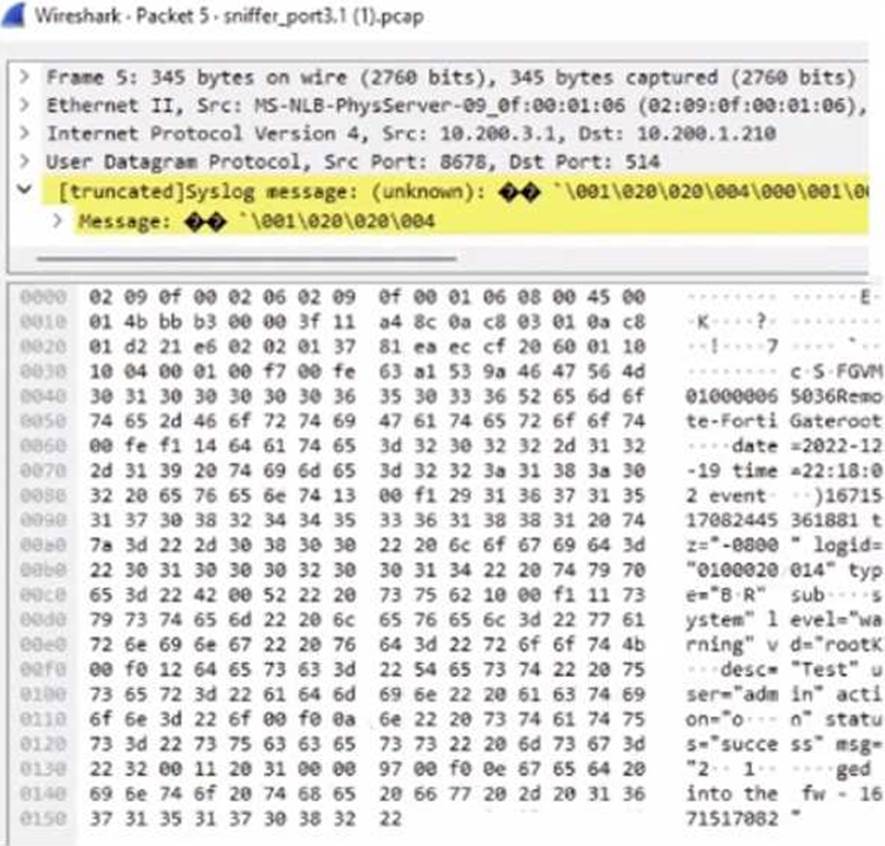

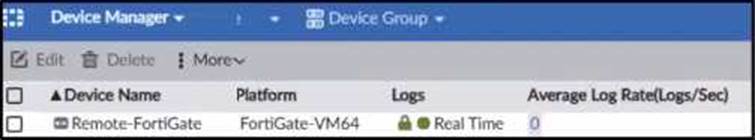
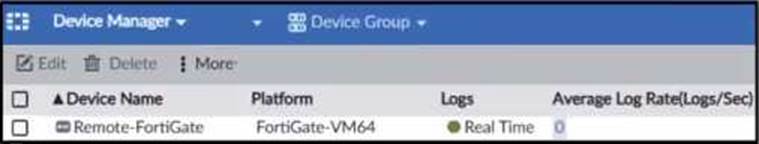
정답:
Explanation:
The exhibit shows a packet capture with a syslog message containing a log event from a FortiGate device. This log event includes several details such as the date, time, and event message. The corresponding image that matches this packet capture would be the one which shows that the FortiGate device has logs being received in real-time, as indicated by the highlighted section in the packet capture where it mentions "real-time". Therefore, Option A is the correct answer because it shows logs with "Real Time" status for the FortiGate-VM64 device, indicating that this FortiAnalyzer is currently receiving real-time logs from the device, matching the activity in the packet capture.
Reference: Based on the provided exhibits and the real-time logging information, correlated with the knowledge from the FortiAnalyzer 7.2 Administrator documentation regarding log reception and device management.
정답:
Explanation:
When only some of the expected logs from a FortiGate device are being received on FortiAnalyzer, it often indicates a configuration issue on the FortiGate side. Proper logging configuration on FortiGate involves specifying what types of logs to generate (e.g., traffic, event, security logs) and ensuring that
these logs are directed to the FortiAnalyzer unit for storage and analysis. If the logging settings on FortiGate are not correctly configured, it could result in incomplete log data being sent to FortiAnalyzer. This might include missing logs for certain types of traffic or events that are not enabled for logging on the FortiGate device. Ensuring comprehensive logging is enabled and correctly directed to FortiAnalyzer is crucial for full visibility into network activities and for the effective analysis and reporting of security incidents and network performance.
정답:
Explanation:
When you move a registered logging device from one ADOM (Administrative Domain) to another in FortiAnalyzer, it's essential to ensure that the analytical logs for the moved device are available in the new ADOM to maintain continuity in reporting and log analysis. The command execute sql-local rebuild-adom <new-ADOM-name> is used specifically for this purpose. Running this command populates the new ADOM with the analytical logs of the moved device, enabling you to generate accurate and comprehensive reports based on the historical data of the device in its new ADOM context. This process ensures that the transition of devices between ADOMs does not lead to a loss of analytical insight or reporting capabilities for the device's traffic and events.
정답:
Explanation:
In systems that support hardware RAID, hot swapping allows for the replacement of a failed disk without shutting down the system. This capability is crucial for maintaining uptime and ensuring data redundancy and availability, especially in critical environments. The RAID controller rebuilds the data on the new disk using redundancy data from the other disks in the array, ensuring no data loss and minimal impact on system performance.
In the context of a FortiAnalyzer unit equipped with hardware RAID support, the optimal approach to addressing a hard disk failure is to perform a hot swap of the disk. Hardware RAID configurations are
designed to provide redundancy and fault tolerance, allowing for the replacement of a failed disk without the need to shut down the system. Hot swapping enables the administrator to replace the faulty disk with a new one while the system is still running, and the RAID controller will rebuild the data on the new disk, restoring the RAID array to its fully operational state.
Reference: FortiAnalyzer 7.2 Administrator Guide - "Hardware Maintenance" and "RAID Management" sections.
정답:
Explanation:
In an HA cluster, the firmware upgrade process involves upgrading the secondary devices first. This approach ensures that the primary device can continue to handle traffic and maintain the operational stability of the network while the secondary devices are being upgraded. Once the secondary devices have successfully upgraded their firmware and are operational, the primary device can then be upgraded. This method minimizes downtime and maintains network integrity during the upgrade process.
When upgrading firmware in a High Availability (HA) cluster of FortiAnalyzer units, the recommended practice is to first upgrade the secondary devices before upgrading the primary device. This approach ensures that the primary device, which coordinates the cluster's operations, remains functional for as long as possible, minimizing the impact on log collection and analysis. Once the secondary devices are successfully upgraded and operational, the primary device can be upgraded, ensuring a smooth transition and maintaining continuous operation of the cluster.
Reference: FortiAnalyzer 7.2 Administrator Guide - "System Administration" and "High Availability" sections.
정답:
Explanation:
On FortiAnalyzer, analytics logs refer to the logs that have been processed, indexed, and then stored in the SQL database. This process allows for efficient data retrieval and analytics. Unlike basic log storage, which might involve simple compression and storage in a file system, analytics logs in FortiAnalyzer undergo an indexing process. This enables advanced features such as quick search, report generation, and detailed analysis, making it easier for administrators to gain insights into network activities and security incidents.
Reference: FortiAnalyzer 7.2 Administrator Guide - "Log Management" and "Data Analytics" sections.
정답:
Explanation:
Link aggregation is a method used to combine multiple network connections in parallel to increase throughput and provide redundancy in case one of the links fail. This feature is used in network appliances, including FortiAnalyzer, to add redundancy to the network connections, ensuring that there is a backup path for traffic if the primary path becomes unavailable.
Reference: The FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 Administration Guide explains the concept of link aggregation and its relevance to

정답:
Explanation:
The configuration displayed in the exhibit indicates that the FortiAnalyzer is set up with a cluster virtual IP address of 192.168.101.222 assigned to interface port1. This setup is typically used for the FortiAnalyzer to receive logs on that interface when operating in a High Availability (HA) configuration. The exhibit does not provide enough information to conclude whether this FortiAnalyzer will be the primary unit in the HA cluster or the duration for the failover trigger; it only confirms the interface configuration for log reception.
Reference: Based on the FortiAnalyzer 7.4.1 Administration Guide, the similar configurations for HA and log reception are discussed, which would be relevant for understanding the settings in FortiAnalyzer 7.2