Certified Pega Decisioning Consultant 8.8 V1 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년03월23일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 Pegasystems PEGACPDC88V1 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 PEGACPDC88V1 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 60개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
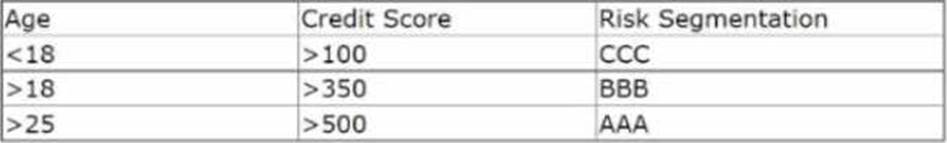
정답:
Explanation:
To implement the business requirement, you need to add a decision table to a decision strategy and pass the credit score as the parameter. A decision table allows you to define rules based on one or more input parameters and return an output value. In this case, you can use the credit score as an input parameter and return the risk category/grade as an output value. You can then use this output value to filter out customers who are not in the low-risk segment (AAA).
Reference: Pega Academy - Decisioning Consultant - Using decision tables
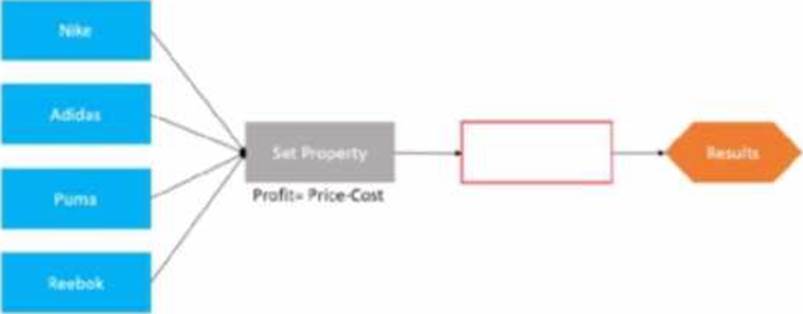
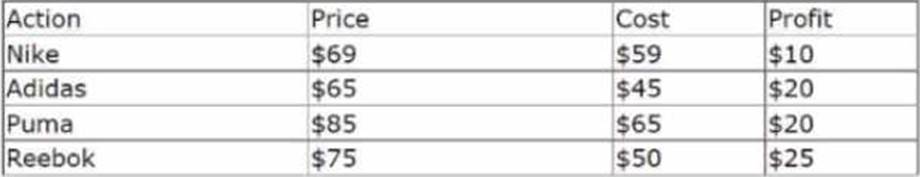
정답:
Explanation:
To output the most profitable shoe, you need to add a Prioritize component in the blank space. A Prioritize component allows you to rank actions based on one or more properties. In this case, you can rank the shoes based on the Profit property and select the highest ranked shoe as the output.
Reference: Pega Academy - Decisioning Consultant - Prioritizing actions
정답:
Explanation:
To access a property from an unconnected component, you use the component-dot-property construct. For example, if you want to access the property. Rank from an unconnected component named ActionRanking, you use ActionRanking.Rank.
Reference: Pega Academy - Decisioning Consultant - Accessing properties from unconnected components
정답:
Explanation:
When you create a new trigger in the Next-Best-Action Designer, Pega Customer Decision Hub automatically generates a decision strategy for that trigger and channel. You do not need to create or modify any strategies manually.
Reference: Pega Academy - Decisioning Consultant - Creating triggers
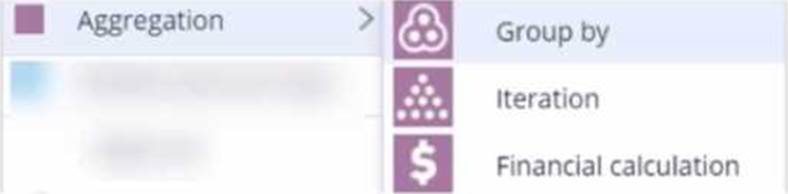
정답:
Explanation:
Aggregation components are used to perform calculations on a list of actions, such as sum, average, count, minimum, or maximum. For example, you can use an aggregation component to calculate the total value of all the actions in a group.
Reference: Pega Academy - Decisioning Consultant - Aggregating actions

정답: 
정답:
Explanation:
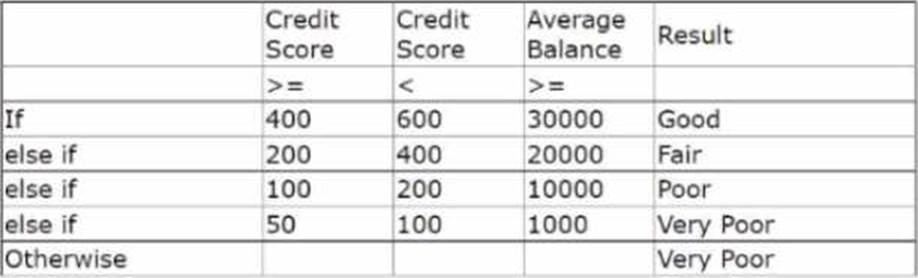
Using the decision table, you can find the label for a customer with a credit score of 240 and an average balance of 35000 by following these steps:
Start from the top row and check if the customer’s credit score is less than 150. If yes, then the label
is Very Poor. If no, then move to the next row.
Check if the customer’s credit score is less than 175 and their average balance is less than 25000. If yes, then the label is Poor. If no, then move to the next row.
Check if the customer’s credit score is less than 200 and their average balance is less than 50000. If yes, then the label is Fair. If no, then move to the next row.
Check if the customer’s credit score is less than 250 and their average balance is less than 75000. If yes, then the label is Good. If no, then move to the last row.
The last row applies to all other cases that do not match any of the previous conditions. The label for this row is Very Poor.
In this case, the customer’s credit score is not less than 150, so the first row does not apply. The customer’s credit score is less than 175, but their average balance is not less than 25000, so the second row does not apply either. The customer’s credit score is not less than 200, so the third row does not apply. The customer’s credit score is less than 250 and their average balance is less than 75000, so the fourth row applies. Therefore, the label for this customer is Poor.

정답: 
정답:
Explanation:
In a decision strategy, to use a customer property in an expression, you need to define Customer page in Pages & Classes and specify its class as Data-Customer. This allows you to access customer properties by using dot notation, such as Customer.Age or Customer.Gender. You do not need to define the property as a strategy property, use it without any prefix, or prefix it with the keyword Customer.
Reference: [Certified Pega Decisioning Consultant | Pega Academy], Decision strategies
정답:
Explanation:
A dotted line from a “Group By” component to a “Filter” component means that a property from the “Group By” is referenced by the “Filter” component. For example, if you group customers by age and then filter them by average spending, you need to reference a property from the “Group By” component, such as .pxSegment, in the “Filter” component. A dotted line does not indicate a one-to-one relationship, an evaluation order, or a copying of information between components
정답:
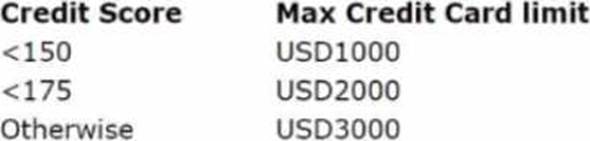
Explanation:
The scorecard model determines the customer credit score based on various factors, such as income, expenses, assets, liabilities, etc. The scorecard model has a Results tab where you can define the cutoff values for different segments based on the credit score. To change the threshold value for the USD2000 credit limit from <175 to <200, you need to change the cutoff value in the Results tab of the scorecard model. Changing the cutoff value in the scorecard decision component, changing the condition in the strategy, or mapping the score value in the decision strategy will not affect the credit score calculation or segmentation.
정답:
Explanation:
The always-on outbound customer engagement paradigm relies on AI to select the best action for each customer at any given time, based on their profile, context, and behavior. You do not need to create separate segments or schedules for different offers or timings. You can configure the primary schedule to run daily and let the AI choose the best action based on engagement policies, such as contact policies, eligibility rules, suitability rules, and arbitration. The AI will also learn from the customer responses and optimize the action selection over time.
정답:
Explanation:
Paul cannot see the Reward card offer because he rejected other credit card offers twice on the web channel and once in contact center in the past 15 days. This triggers the first contact policy that suppresses a group of credit card offers for 30 days if any credit card offer is rejected three times in any channel in the past 15 days. The Reward card offer is part of the credit card group, so it is suppressed for Paul for 30 days. The second contact policy that suppresses the Reward card offer for 7 days if it is rejected twice in any channel in the last 7 days does not apply because Paul did not reject the Reward card offer twice in any channel in the last 7 days.
Reference: [Certified Pega Decisioning Consultant | Pega Academy], Suppression policies system Following is the description of the image that was sent with question no:5: This is a screenshot of a table with four columns and two rows.
The table has a header row with white text on a blue background.
The header row reads “Constraint name”, “Constraint mode”, “Constraint value”, and “Channel”.
The second row has black text on a white background.
The second row reads “Standard card”, “Return any action that does not exceed”, “100”, and “Daily”.
The table has a gray border and a light blue background.
정답:
Explanation:
Volume constraints allow you to limit the number of times an action is presented to customers across one or more channels. You can use volume constraints to implement the requirement that customers do not receive more than four promotional emails per quarter, regardless of past responses to that action by the customer. You can configure the volume constraint to limit the number of actions per channel per quarter and select the option to ignore previous responses. Outbound channel limits are used to limit the number of customers contacted per channel per run, not per quarter. Suppression policies are used to exclude customers from receiving an action based on certain conditions, such as opt-out preferences or recent purchases, not based on the number of times the action is presented. Suitability rules are used to determine whether an action is suitable for a customer based on their propensity, priority, or other criteria, not based on the number of times the action is presented.
정답:
Explanation:
A suppression policy allows you to define conditions that prevent customers from receiving an action or a group of actions. You can use a suppression policy to implement the requirement that customers do not see home loan offers on their account page if they have already received three home loan offers in the last two weeks. You can configure the suppression policy to suppress the home loan group based on the number of times the customer received any action from that group in the past 14 days. Applicability rules are used to determine whether an action is relevant for a customer based on their profile or context, not based on the number of times they received an action. Customer contact limits are used to limit the number of times a customer can be contacted per channel per time period, not based on the number of times they received an action. Volume constraints are used to limit the number of times an action is presented to customers across one or more channels, not based on the number of times they received an action.
Reference: [Certified Pega Decisioning Consultant | Pega Academy], Suppression policies