HashiCorp Certified: Vault Associate (003) 온라인 연습
최종 업데이트 시간: 2025년03월23일
당신은 온라인 연습 문제를 통해 HashiCorp VA-003-P 시험지식에 대해 자신이 어떻게 알고 있는지 파악한 후 시험 참가 신청 여부를 결정할 수 있다.
시험을 100% 합격하고 시험 준비 시간을 35% 절약하기를 바라며 VA-003-P 덤프 (최신 실제 시험 문제)를 사용 선택하여 현재 최신 57개의 시험 문제와 답을 포함하십시오.
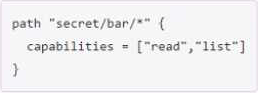



정답:
Explanation:
This policy will allow the user to read all the secrets in the read path and list all the secrets in that path. The asterisk (*) here is a wildcard that indicates all possible subpaths under the path. Such a policy setup ensures that the user can not only list all the secrets, but also read each one. secret/bar/*
정답:
Explanation:
In Vault, permission is required to view or output all endpoints under a path. The permission allows the role to view all key names under the path, but does not provide the content of the key. “list”
정답:
Explanation:
An orphan token is a token that cannot be cascaded to be revoked when its parent token is revoked. Typically, when a parent token is revoked, all child tokens created by it are also revoked. However, orphan tokens are an exception, as they do not have this parent-child association and therefore remain active when the parent token is revoked.
정답:
Explanation:
The maximum time-to-live (TTL) for a token is defined by the lowest value among the following factors:
The authentication method that issued the token. Each auth method can have a default and a maximum TTL for the tokens it generates. These values can be configured by the auth method’s mount options or by the auth method’s specific endpoints.
The mount endpoint configuration that the token is accessing. Each secrets engine can have a default and a maximum TTL for the leases it grants. These values can be configured by the secrets engine’s
mount options or by the secrets engine’s specific endpoints.
A parent token TTL. If a token is created by another token, it inherits the remaining TTL of its parent token, unless the parent token has an infinite TTL (such as the root token). A child token cannot outlive its parent token.
System max TTL. This is a global limit for all tokens and leases in Vault. It can be configured by the system backend’s max_lease_ttl option.
The client system that uses the token cannot define the maximum TTL for the token, as this is determined by Vault’s configuration and policies. The client system can only request a specific TTL for the token, but this request is subject to the limits imposed by the factors above.
Reference:
https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/concepts/tokens3, https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/concepts/lease2, https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/commands/auth/tune4, https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/commands/secrets/tune5, https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/commands/token/create6
정답:
Explanation:
Dynamic secrets are generated on-demand by Vault and have a limited time-to-live (TTL). They do not ensure that administrators can see every password used, as they are often encrypted and ephemeral.
The benefits of dynamic secrets are:
They support systems that do not natively provide a method of expiring credentials, such as databases, cloud providers, SSH, etc. Vault can revoke the credentials when they are no longer needed or when the lease expires.
They minimize the damage of credentials leaking, as they are short-lived and can be easily rotated or revoked. If a credential is compromised, the attacker has a limited window of opportunity to use it before it becomes invalid.
They replace cumbersome password rotation tools and practices, as Vault can handle the generation and revocation of credentials automatically and securely. This reduces the operational overhead and complexity of managing secrets.
Reference:
https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/tutorials/getting-started/getting-started-dynamic-secrets1, https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/concepts/lease2
정답:
Explanation:
The Google Cloud Secrets Engine is the best option for the DevOps team to provision VMs in GCP via a CICD pipeline and integrate Vault to protect the credentials used by the tool. The Google Cloud Secrets Engine can dynamically generate GCP service account keys or OAuth tokens based on IAM policies, which can be used to authenticate and authorize the CICD tool to access GCP resources. The credentials are automatically revoked when they are no longer used or when the lease expires, ensuring that the credentials are short-lived and secure. The DevOps team can configure rolesets or static accounts in Vault to define the scope and permissions of the credentials, and use the Vault API or CLI to request credentials on demand. The Google Cloud Secrets Engine also supports generating access tokens for impersonated service accounts, which can be useful for delegating access to other service accounts without storing or managing their keys1.
The Identity Secrets Engine is not a good option for this use case, because it does not generate GCP credentials, but rather generates identity tokens that can be used to access other Vault secrets engines or namespaces2. The Key/Value Secrets Engine version 2 is also not a good option, because it does not generate dynamic credentials, but rather stores and manages static secrets that the user provides3. The SSH Secrets Engine is not a good option either, because it does not generate GCP credentials, but rather generates SSH keys or OTPs that can be used to access remote hosts via SSH4.
Reference: Google Cloud - Secrets Engines | Vault | HashiCorp Developer Identity - Secrets Engines | Vault | HashiCorp Developer KV - Secrets Engines | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
SSH - Secrets Engines | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
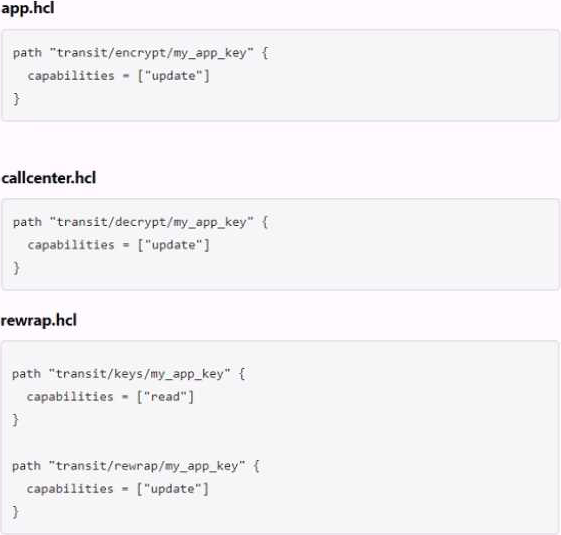
정답:
Explanation:
These policies allow organizations to:
Separates permissions allowed on actions associated with the transit secret engine
Here's how to do it:
app.hcl The policy allows the entity to perform cryptographic operations using a specific key () of the Transit secret engine.my_app_key
callcenter.hcl The policy allows decryption operations to be performed on the same.my_app_key
rewrap.hcl Policies allow the key to be read and the data to be reencapsulated, which essentially decrypts and re-encrypts the data without displaying plaintext, which is useful for rotating the underlying encryption key.
Each policy targets specific operations of the Transit secret engine, enabling fine-grained access control to encryption, decryption, and key management functions. This is important for maintaining a strict separation of duties within the organization.
정답:
Explanation:
This command is a command to log in to Vault using the LDAP method. Usually, after executing this command, the user is prompted to enter their password, rather than the command immediately failing because the password was not provided.vault login -method=ldap username=mitchellh
정답:
Explanation:
Option A. VAULT_ADDR is an environment variable that overrides the CLI's default Vault server address.
This environment variable can be set to the URL of the Vault server, which is used by Vault's CLI tool to communicate with the Vault server.
정답:
Explanation:
Using a short-lived dynamic secrets can help limit the scope of a credential breach by reducing the
exposure time of the secrets. Dynamic secrets are generated on-demand by Vault and automatically revoked when they are no longer needed. This way, the credentials are not stored in plain text or in a static database, and they can be rotated frequently to prevent unauthorized access. Dynamic secrets also provide encryption as a service, which means that they perform cryptographic operations on data in-transit without storing any data. This adds an extra layer of security and reduces the risk of data leakage or tampering.
Reference: Dynamic secrets | Vault | HashiCorp Developer, What are dynamic secrets and why do I need them? - HashiCorp
정답:
Explanation:
The vault kv put command writes the data to the given path in the K/V secrets engine. The command requires the mount path of the K/V secrets engine, the secret path, and the key-value pair to store. The mount path can be specified with the -mount flag or as part of the secret path. The key-value pair can be given as an argument or read from a file or stdin. The correct syntax for the command is: vault kv put -mount=secret my-secrets/my-password 53cr3t or
vault kv put secret/my-secrets my-password=53cr3t
The other options are incorrect because they use the deprecated vault kv write command, or they have the wrong order or format of the arguments.
Reference: https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/commands/kv/put3, https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/commands/kv4
정답:
Explanation:
Not all storage backends support high availability mode for Vault. Only the storage backends that support locking can enable Vault to run in a multi-server mode where one server is active and the others are standby. Some examples of storage backends that support high availability mode are Consul, Integrated Storage, and ZooKeeper. Some examples of storage backends that do not support high availability mode are Filesystem, MySQL, and PostgreSQL.
Reference:
https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/concepts/ha1, https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/configuration/storage2
정답:
Explanation:
The command that does not meet the security requirement of not having secrets appear in the shell history is B. vault kv put secret/password value-itsasecret. This command would store the secret value “itsasecret” in the key/value secrets engine at the path secret/password, but it would also expose the secret value in the shell history, which could be accessed by other users or malicious actors. This is not a secure way of storing secrets in Vault.
The other commands are more secure ways of storing secrets in Vault without revealing them in the
shell history.
A. generate-password | vault kv put secret/password value would use a pipe to pass the
output of the generate-password command, which could be a script or a tool that generates a
random password, to the vault kv put command, which would store the password in the key/value
secrets engine at the path secret/password. The password would not be visible in the shell history,
only the commands.
C. vault kv put secret/password [email protected] would use the @ syntax to
read the secret value from a file named data.txt, which could be encrypted or protected by file
permissions, and store it in the key/value secrets engine at the path secret/password. The file name
would be visible in the shell history, but not the secret value.
D. vault kv put secret/password value-
SSECRET_VALUE would use the -S syntax to read the secret value from the environment variable
SECRET_VALUE, which could be set and unset in the shell session, and store it in the key/value
secrets engine at the path secret/password. The environment variable name would be visible in the
shell history, but not the secret value.
Reference: [Write Secrets | Vault | HashiCorp Developer]
정답:
Explanation:
AppRole is a machine-oriented authentication method that allows machines or applications to authenticate with Vault using a role ID and a secret ID. The role ID is a unique identifier for the application, and the secret ID is a single-use credential that can be delivered to the application securely. AppRole is designed to provide secure introduction of machines and applications to Vault, and to support the principle of least privilege by allowing fine-grained access control policies to be attached to each role1.
Okta, GitHub, and Transit are not machine-oriented authentication methods. Okta and GitHub are user-oriented authentication methods that allow users to authenticate with Vault using their Okta or GitHub credentials23. Transit is not an authentication method at all, but a secrets engine that provides encryption as a service4.
Reference: AppRole Auth Method | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
Okta Auth Method | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
GitHub Auth Method | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
Transit Secrets Engine | Vault | HashiCorp Developer
정답:
Explanation:
The Vault CLI command to query information about the token the client is currently using is vault token lookup. This command displays information about the token or accessor provided as an argument, or the locally authenticated token if no argument is given. The information includes the token ID, accessor, policies, TTL, creation time, and metadata. This command can be useful for debugging and auditing purposes, as well as for renewing or revoking tokens.
Reference: token lookup - Command | Vault | HashiCorp Developer, Tokens | Vault | HashiCorp Developer